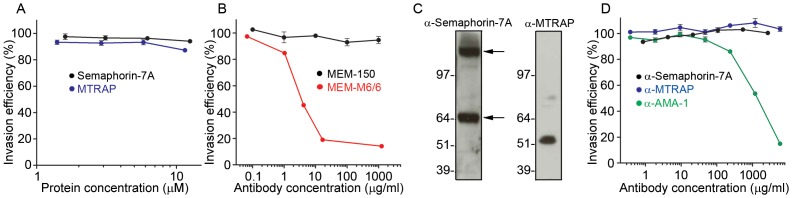
Figure 6. Attempts to block the MTRAP-Semaphorin-7A interaction has no effect on erythrocyte invasion.
(A) Recombinant Semaphorin-7A and MTRAP have no inhibitory effect on erythrocyte invasion. Purified pentamerised Semaphorin-7A or MTRAP were added to P. falciparum erythrocyte invasion assays at concentrations that exceeded the monomeric equilibrium affinity constant by a factor of 10. (B) Monoclonal anti-Semaphorin-7A antibody has no effect on erythrocyte invasion. Monoclonal anti-Semaphorin-7A (MEM-150) and an anti-basigin positive control (MEM-M6/6) were added to P. falciparum erythrocyte invasion assays in increasing concentrations. MEM-M6/6 showed clear inhibition of invasion, whereas MEM-150 had no observable effect. (C) Rabbit polyclonal antibodies against purified monomeric MTRAP and Semaphorin-7A bind native MTRAP and Semaphorin-7A. Erythrocyte ghosts (left blot) and parasite supernatants (right blot) were analysed by Western blot under non-reducing conditions, and detected by incubation with purified polyclonal antibodies, followed by an anti-rabbit-IgG-HRP antibody. The predicted monomer molecular weights of native Semaphorin-7A and MTRAP are 79.3 and 55.6 kDa respectively. The top arrow indicates the dimer and the bottom arrow the monomer of Semaphorin-7A. (D) Polyclonal antibodies against MTRAP and Semaphorin-7A do not inhibit erythrocyte invasion. Purified polyclonal antibodies against MTRAP and Semaphorin-7A were added to P. falciparum erythrocyte invasion assays but did not affect the efficiency of invasion relative to a positive control (anti-AMA-1).