Figure 8.
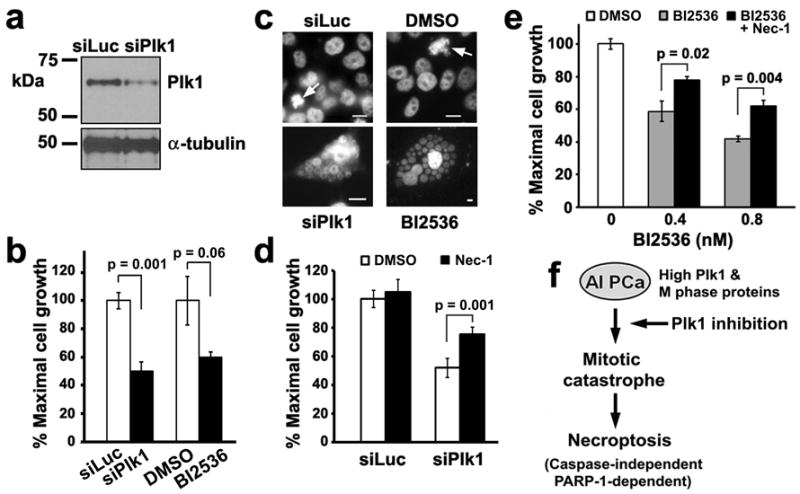
Necrostatin-1 attenuates cell death by necroptosis resulting from either Plk1 depletion or Plk1 inhibition in LNCaP-AI cells. (a) LNCaP-AI cells were transfected with either siLuciferase or Plk1 RNAi oligos for 5 days. Cell lysates (20 μg) were analyzed for Plk1 levels. α-tubulin was used as a loading control. (b) Cells prepared as in (a) or treated with 0.8 nM BI2536 were analyzed after 5 days by an MTS assay. Triplicate samples (mean ± SD) from one of n = 2 experiments are shown. (c) Cells were treated as in (b) and counterstained with DAPI to visualize DNA, shown here in black and white for contrast. Arrows, cells in mitosis in control cultures. Single giant cells containing clusters of nuclear vesicles are shown for siPlk1 and BI2536-treated LNCaP-AI cells. Bars, 10 μm. Note differences in scale. (d) Cells were transfected with siPlk1 for 5 days. 7.7 μM Necrostatin-1 (Nec-1), the necroptosis inhibitor, was added 3 h prior to siPlk1 transfection and remained throughout the experiment. Triplicate samples (mean ± SD) from MTS assays from one of n = 2 experiments are shown. (e) Cells were treated with 0.4 or 0.8 nM BI2536 for 5 days. 5 μM Nec-1 was added 3 h prior to BI2536 addition and remained throughout the experiment. Triplicate samples (mean ± SD) from MTS assays from one of n = 3 experiments are shown. (f) Working model of necroptosis induction by Plk1 inhibition in androgen-insensitive PCa cells. See text.
