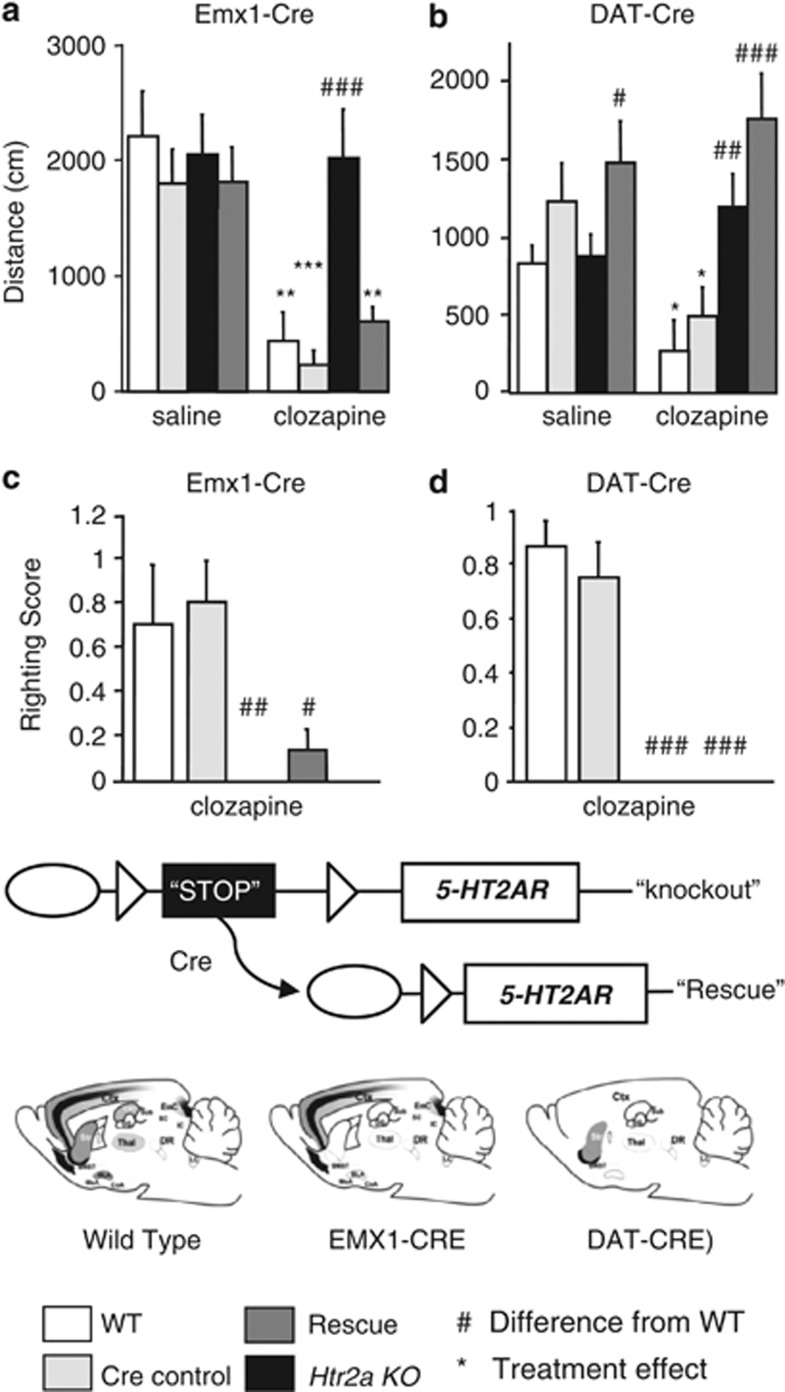
Figure 5.
As found previously, clozapine dramatically reduced locomotor activity in wild-type (WT) mice (a) (N=7) as well as in Cre control mice (N=8). The locomotor behavior of serotonin 2A (5-HT2A) knockout (KO) mice was unaffected by clozapine treatment (N=7); however, mice expressing htr2ar in the cortex (N=7 saline, 8 clozapine treated) behaved like WT mice, showing decreased locomotor activity following clozapine treatment. (b) At baseline, 5-HT2A-DAT-Cre rescue mice showed slightly elevated baseline activity. Clozapine attenuated this locomotion in WT and DAT-Cre control mice; however, it did not affect the activity of KO (n=11) or 5HT2A-DAT mice (N=15). (c) Clozapine impaired the righting reflex in WT mice (N=7) and EMX1-Cre control mice (N=8). Righting reflex was not impaired in KO mice following clozapine (N=7) nor was it impaired in 5-HT2A-EMX1-Cre mice (N=7). (d) In a subsequent cohort of mice, we again observed impaired righting reflex in WT (n=15) and DAT-Cre control mice (N=12). KO mice were resistant to this response (N=11) as were 5-HT2A-DAT-Cre rescue mice (N=15). No significant genotype effects were observed in saline-treated mice as none of the groups displayed impaired righting reflex (data not shown). Data are shown as mean±SEM. **P<0.01, ***P<0.0001 difference from vehicle treatment. #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.0001 indicates a significant difference in behavior of the KO relative to WT mice under the same treatment regimen.