Figure 2.
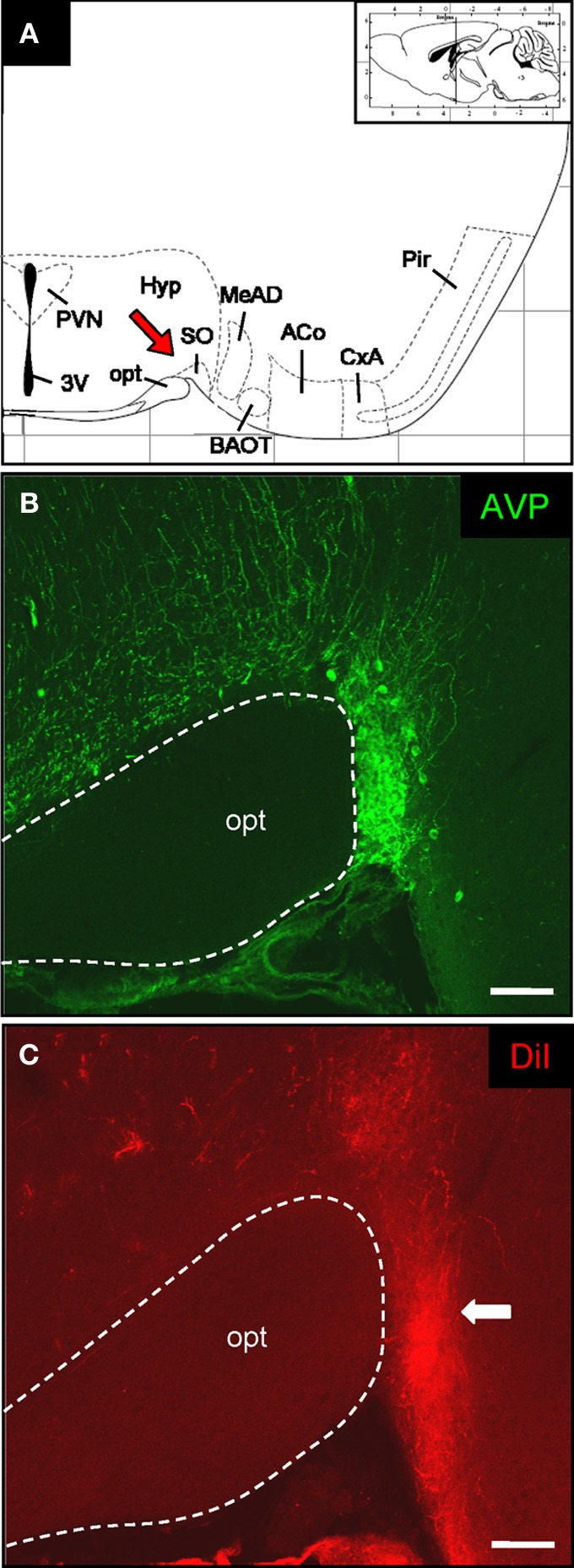
DiI-labeled fibers in the supraoptic nucleus of the hypothalamus. (A) Schematic representation of a section through the mouse brain [adapted from Paxinos and Franklin (2001)]. The position of the section along the anterior–posterior axis is indicated on the inset. The interval of the lattice is 1 mm. Several distinct nuclei are indicated. The red arrow highlights the supraoptic nucleus. 3V, third ventricle; ACo, anterior cortical amygdala; BAOT, bed nucleus of the accessory olfactory tract; CxA, cortex-amygdala transition zone; MeAD: medial amygdala anterior-dorsal part; opt, optic tract; Pir, piriform cortex; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; SO: supraoptic nucleus. (B) Confocal image of a cross section through the supraoptic nucleus. Vasopressinergic cells are stained with a specific antibody (anti-neurophysin-vasopressin). According to this cell population the position of this particular hypothalamic nucleus close to the optic tract can be exactly determined. Pinhole size: 70 μm. Scale bar: 100 μm. (C) After application of DiI onto the OR37 glomerulus a prominent bundle of labeled fibers can be visualized on the neighboring tissue section. Comparing the two staining patterns shows that the DiI-labeled fibers extend up to the somatic portion of the supraoptic nucleus (arrow). Pinhole size: 80 μm. Scale bar: 100 μm.
