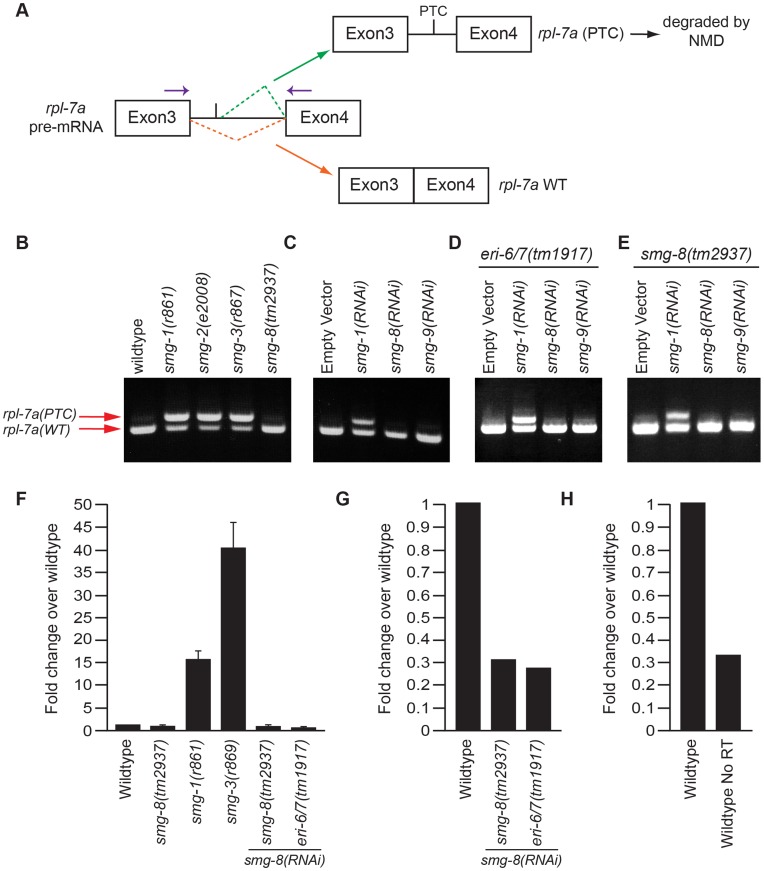
Figure 2. smg-8 lacks an NMD phenotype for the native NMD target rpl-7a.
(A) Schematic representation of the two alternatively spliced isoforms of rpl-7a. The isoform containing the premature termination codon (PTC) is subject to degradation by NMD, whereas the shorter isoform is not. RT-PCR was performed using a pair of primers that distinguish the two spliced isoforms (purple arrows). (B) The upper, PTC band is visible only when the NMD pathway is compromised by smg-1, smg-2 or smg-3 mutations (lanes 2, 3 and 4). Only the lower WT band is observed in wild-type (lane 1) and smg-8 mutant (lane 5) animals. (C) Wild-type worms were fed bacteria expressing dsRNA targeting smg-1, smg-8 or smg-9 from the Ahringer dsRNA library [26]. RNA was analyzed as in (B). (D) An enhanced RNAi mutant strain eri-6/7 [22], [23] was used and RNAi conducted as in (C). RNA was analyzed as in (B). (E) As in D, using the smg-8(tm2937) mutant strain. (F) RT-qPCR using primers flanking the PTC-containing isoform of rpl-7a, mRNA levels were calculated using the delta-delta-CT method, relative to the control gene pmp-3 [27]. Fold enrichment of the PTC mRNA was normalized to 1 for wild-type. The smg-1 and smg-3 mutants show an enrichment of 15 and 38 fold, respectively. In contrast, in smg-8 mutants, the accumulation of the PTC containing isoform is similar to wild-type (0.7 fold enrichment). smg-8 and eri-6/7 mutant worms treated with smg-8 RNAi show 0.7 and 0.4 fold enrichment, respectively. (G) RT-qPCR to quantify smg-8 RNA. mRNA levels were calculated using the delta-delta-CT method, relative to the control gene pmp-3 [27]. Fold enrichment was normalized to 1 for wild-type. smg-8 and eri-6/7 worms treated with smg-8 RNAi show 0.3 and 0.26 fold enrichment, respectively. (H) As in (G) for wild-type animals and a negative control that lacked Reverse Transcriptase (No RT). Fold enrichment was normalized to 1 for wild-type. No RT control shows 0.3 fold enrichment.