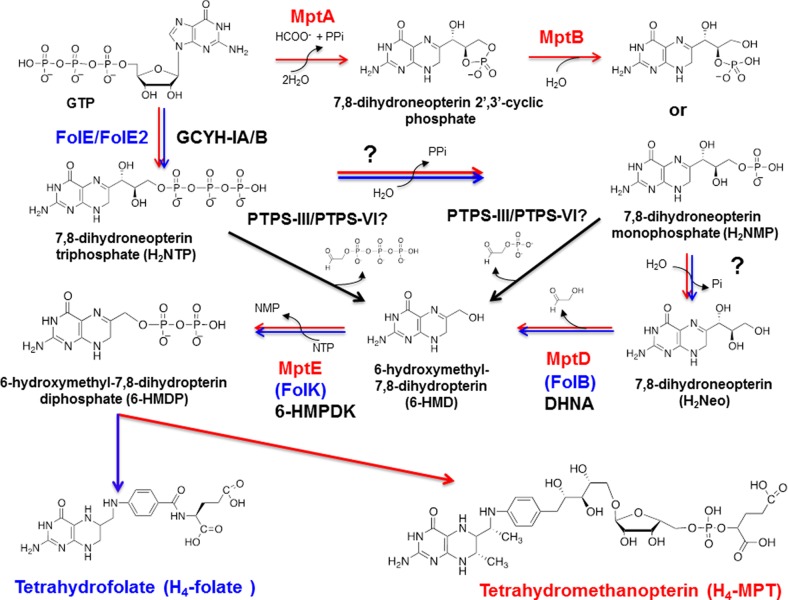
Figure 1.
Early steps of tetrahydrofolate and tetrahydromethanopterin pathways in Bacteria and Archaea. Most bacteria use the FolE (or FolE2)/FolB/FolK route (in blue) to 6-HMDP even if some use the bacterial PTPS-III shunt (in green). Several routes to the common 6-HMDP intermediate in tetrahydrofolate and tetrahydromethanopterin are found in Archaea. A common pathway is the FolE2/MptD/MptE route (in red) such as in H. volcanii paralleling the bacterial pathway. However, some methanogens such as M. jannaschii use the MptA/MptB/MptD/MptE route, whereas P. furiosus uses the archaeal PTPS-III shunt. Phosphatases still to be identified are noted by a question mark (?). FolE/FolE2, GTP cyclohydrolase IA/IB (GCYH-IA/B); FolB, 7,8-dihydroneopterin aldolase (DHNA); FolK, 7,8-dihydro-6-hydroxymethylpterin diphosphokinase (6-HMDPK); MptA, archaeal GTP cyclohydrolase I (Fe(II)-dependent enzyme); MptB, Fe(II) dependent-cyclic phosphodiesterase; MptD, archaeal specific DHNA; MptE, archaeal specific 6-HMDPK; PTPS-III/PTPS-V/PTPS-VI, pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase paralogs involved in 6-HMDP synthesis.