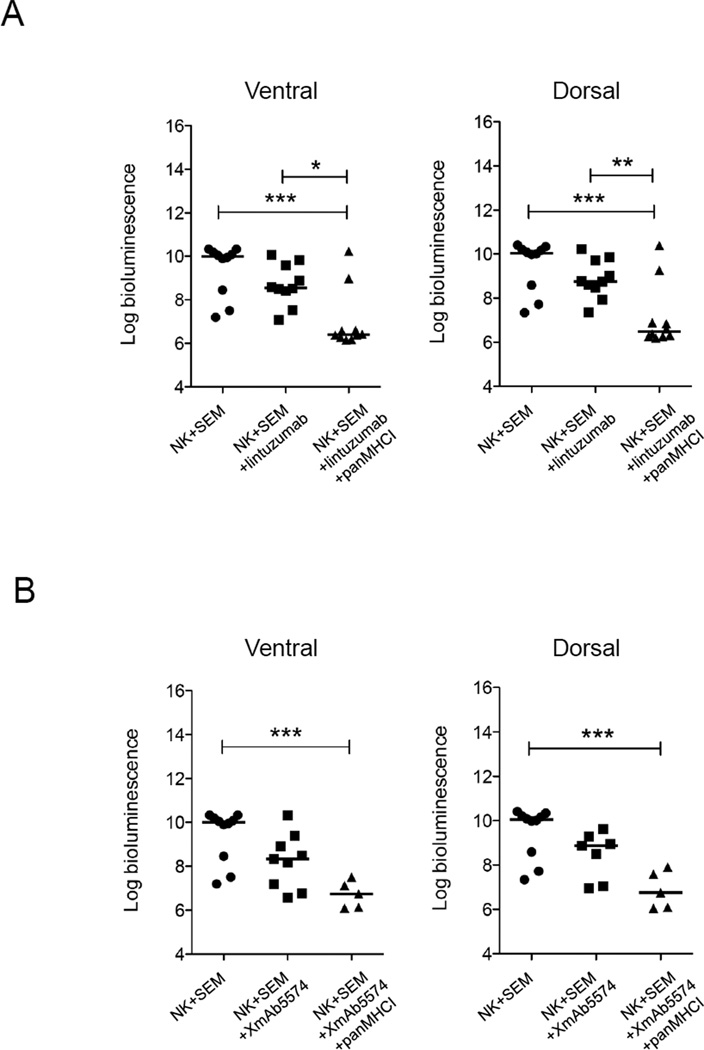
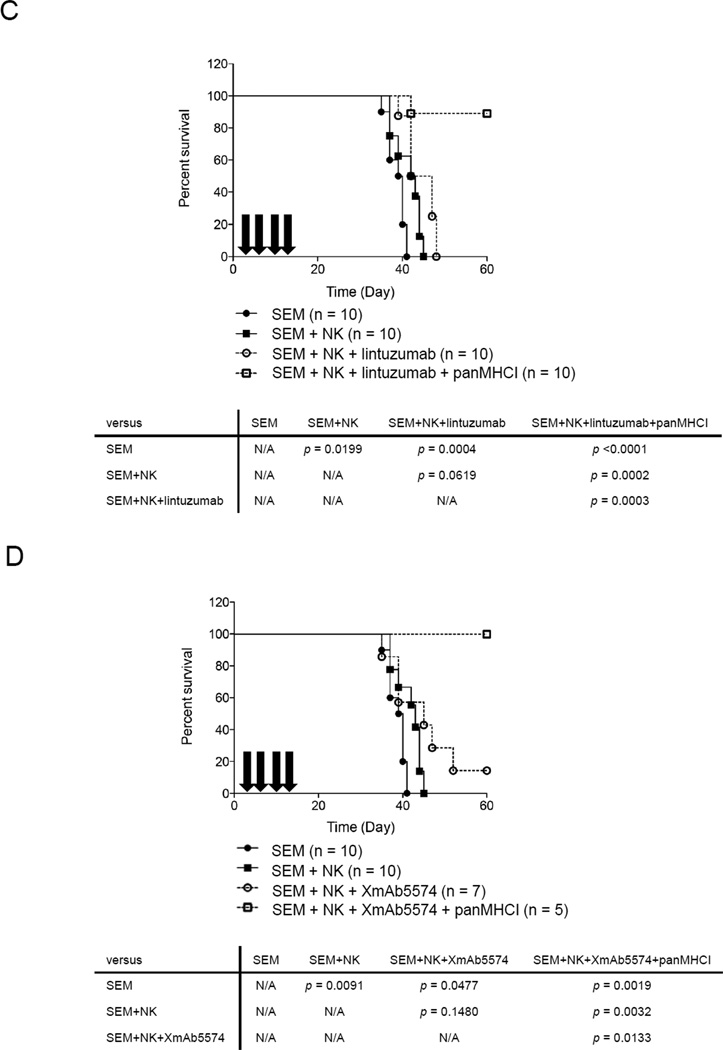
Figure 6.
ADCC with or without interruption of KIR-HLA interaction decreased the rate of leukemia progression and improved disease-free survival in an MLL-rearranged leukemia mouse model. The bioluminescence signals (photons/second) from the ventral and dorsal side of mice of different treatment groups 15 days after treatment with (A) NK (n=10), NK+lintuzumab (n=9), or NK+lintuzumab+panMHCI (n=10). (B) Treatment with NK (n=10), NK+XmAb5574 (n=9), or NK+XmAb5574+panMHCI (n=5). In all cases, 0.5 mg/kg panMHCI antibody was used together with lintuzumab and XmAb5574 as indicated. The bioluminescence signals values were log10 transformed. One-way ANOVA was used to compare the statistical significance between groups. *p<0.05 **p<0.01 ***p<0.001. (C) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of SEM-engrafted mice that received no treatment (closed circle), NK cells alone (closed square), NK+lintuzumab (open circle), or NK+lintuzumab+panMHCI (open square). Arrows represent the timing of antibody injections. Mouse survival was followed for 60 days. (D) The Kaplan-Meier survival curve for the mice that received NK cells with or without XmAb5574 and panMHCI are shown. N/A: not applicable.