Fig. 5.
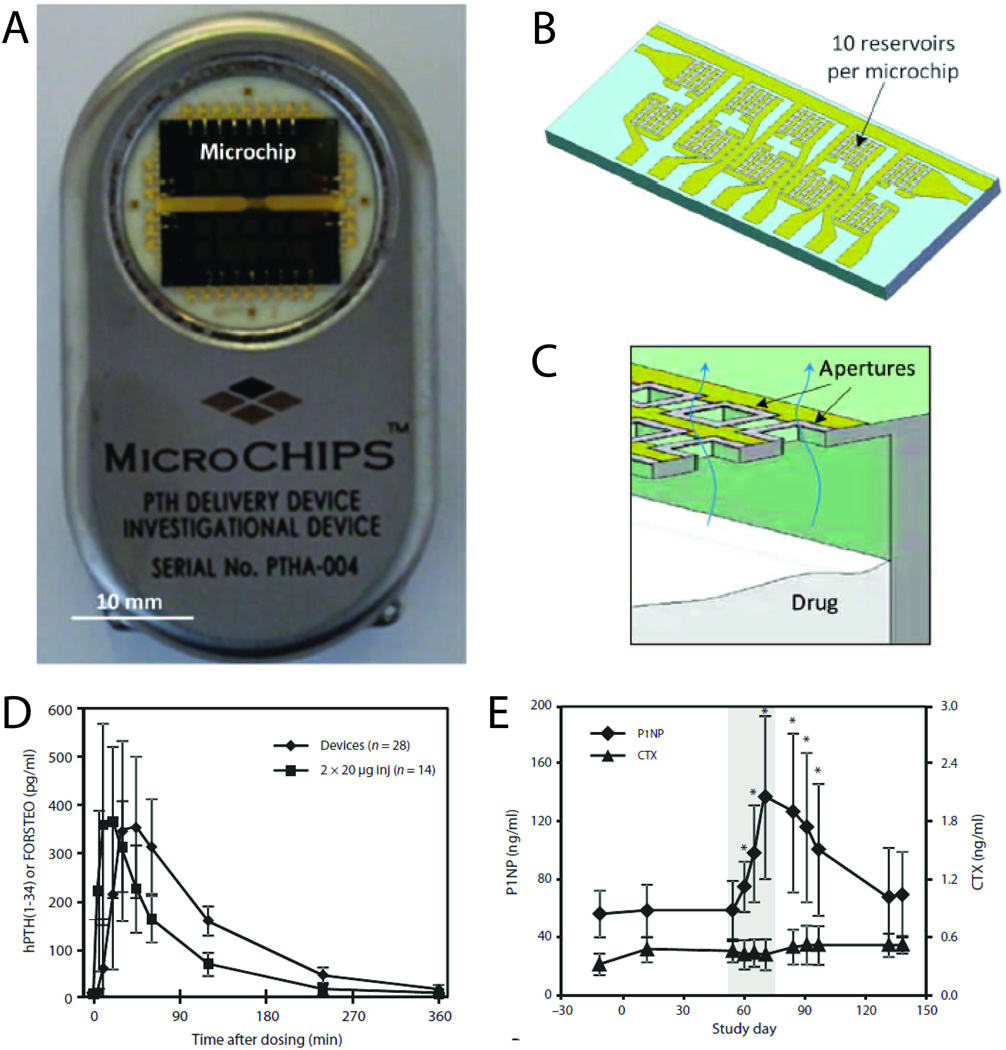
Wirelessly-triggered drug delivery device developed by MicroCHIPS, Inc. (A and B) Implantable drug delivery device (54 mm × 31 mm × 11 mm, l × w × h) (A) containing two microchips with 10 reservoirs each (B). (C) Cross-section schematic of a microchip assembly showing drug release from a single reservoir. (D) Mean plasma concentration of hPTH versus time after release of 40-µg dose from the implanted microchip device (N = 7 patients × four doses) and injection of 2×20-µg doses of FORSTEO (N = 7 patients × two doses). Data are means ± SD. (E) P1NP and CTX bone marker concentrations in serum before, during and after implant-mediated drug dosing. The shaded area encloses the 2 weeks during which individual 40-µg doses of hPTH were released from the implant once daily. Data are means ± SD (N = 7). *P < 0.05 compared to day – 12, pairwise t test. Adapted with permission from ref. 10. Copyright 2012 Science Publishing Group.
