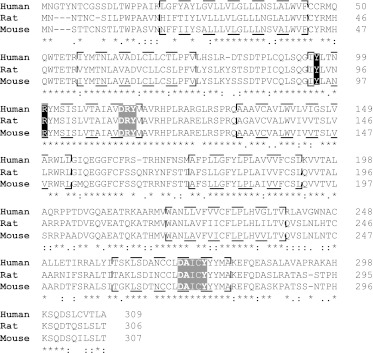
Fig. 13.
Sequence alignment of human, mouse, and rat orthologs of GPR35. The sequence of the short isoform of human GPR35 is aligned with the mouse and rat orthologs. Asterisks indicate amino acid identity across these orthologs, and colons indicate conservative and full-stop semiconservative substitutions between species. Potential transmembrane domains are boxed. The DRY domain and the NPXXY region (light shading), two defining sequence elements of rhodopsin-like, class A GPCRs are highlighted, as are arginine (R) 3.36 and tyrosine (Y) 3.32 (dark shading). Mutation of either of these residues to alanine (Jenkins et al., 2011) eliminates the function of all GPR35 agonists for which this has been assessed (MacKenzie et al., 2011). As such, these residues probably contribute to the ligand binding pocket.