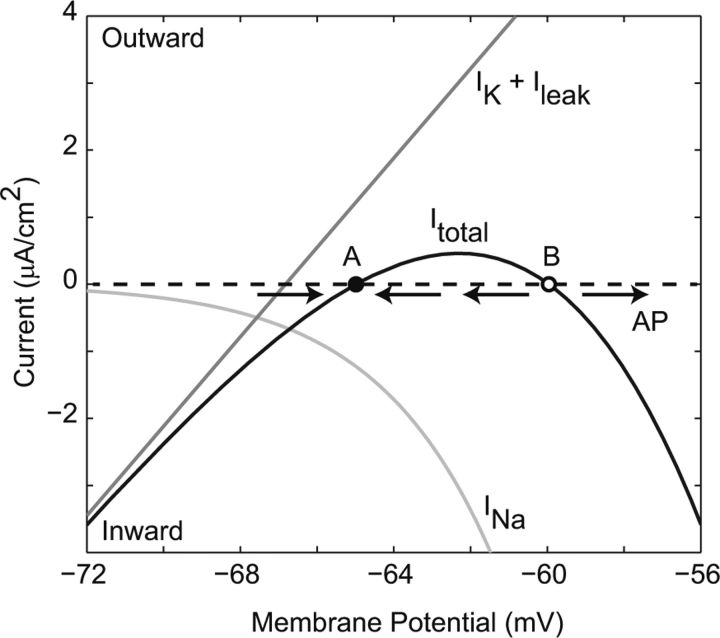
Figure 2.
The nature of excitability in the Hodgkin-Huxley model. The total membrane current (Itotal) [the sum of steady-state sodium current (INa) and the resting-conductance potassium and leak currents (IK + Ileak)], crosses zero at two points, A (resting potential) and B (threshold). See explanation in the main text. In Hodgkin-Huxley terminology, this could be expressed as Itotal = ḡKn∞4(−65)[V − EK] + ḡNam∞3(V)h∞(V)[V − ENa] + gleak[V − Eleak). If the membrane potential is perturbed only a little from rest, the direction of membrane current is such that it is attracted back to A, while if it exceeds the unstable fixed point B, then the membrane potential has a positive derivative, driving it further away from B, and an action potential (AP) is generated.