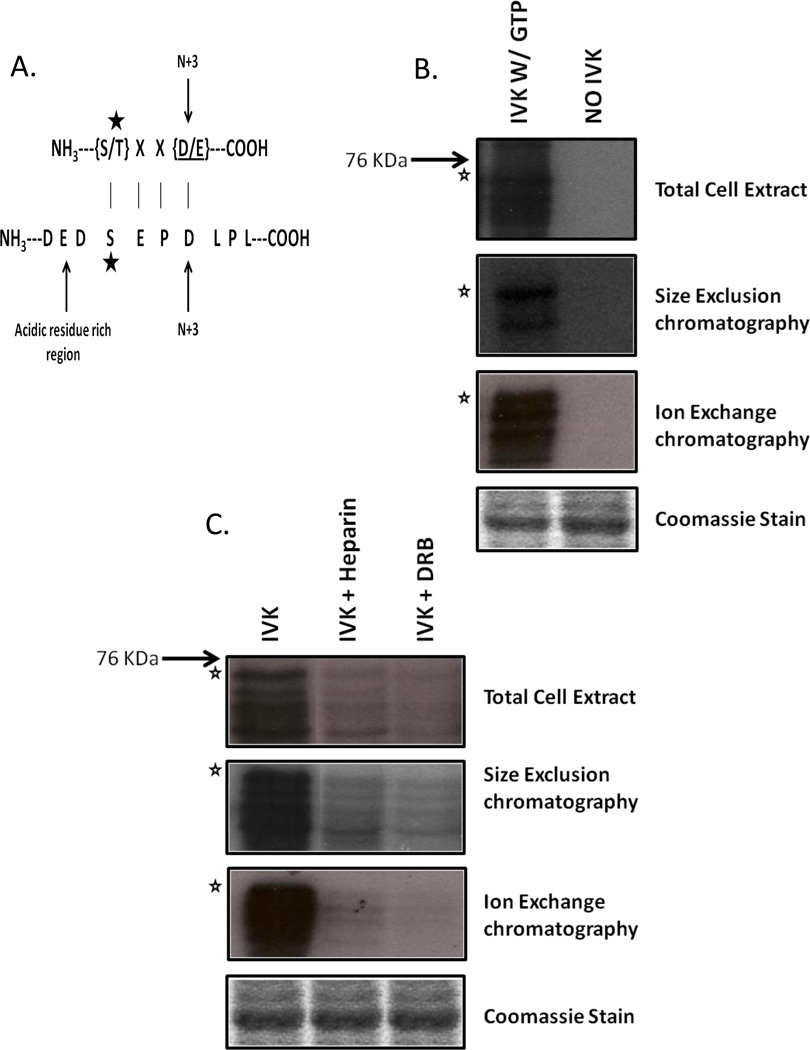
Figure 2.
Identification of CK2 as the Ser209-specific kinase. (A) Ser209 is present in the context of a CK2 recognition site. The star indicates the phosphorylated amino acid. (B) Bacterially expressed GST-Pax3[AAS] was incubated with 25 l of total cell extracts or pooled fractions from size exclusion, or ion exchange separations in the presence of radiolabeled GTP. In vitro kinase assays were carried out, as described in the Materials and Methods. (C) Aliquots from total cell extracts, size exclusion chromatography, or anion exchange chromatography were pre-incubated with the CK2-specific inhibitors Heparin or 5,6-dichloro-1- -D-ribofuranosyl- 1H- benzimidazole (DRB) after which in vitro kinase assays were carried out, as described in the Materials and Methods. In all panels the star indicates the mobility of the GST-Pax3[AAS] with lower bands representing commonly seen degradation products. Equal loading is indicated by Coomassie staining.