Figure 2.
Remodeling of A1/A2 Splice Variant Combinations by Activity Deprivation
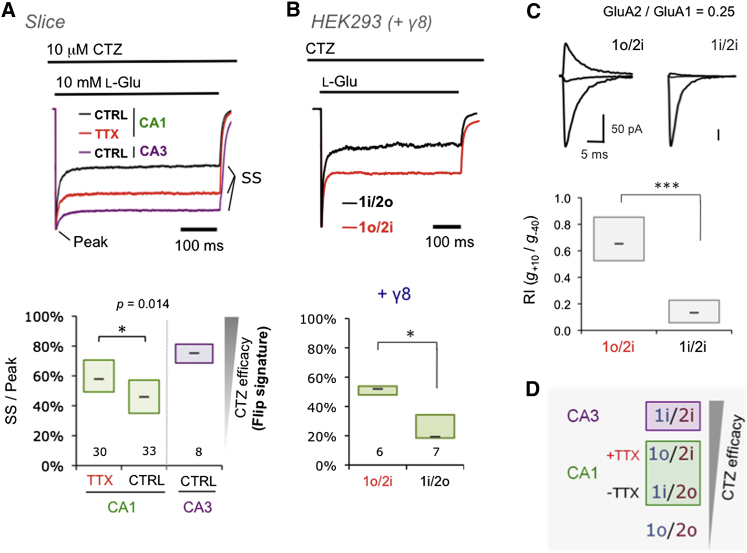
(A) Current traces showing CTZ (10 μM) potentiation of the steady-state (SS) AMPAR current evoked with a 500 ms application of L-Glu (10 mM) (top). Traces are normalized to the peak current. The CTZ efficacy for patches from CA3 pyramidal cells is higher than that of CA1. CTZ efficacy in CA1 is elevated after 48 hr TTX. Data are summarized for all slices (bottom). The number below each box indicates the number of patches. Mann-Whitney U test, ∗p < 0.05. (B) The same experiment as described for (A) (but with 20 μM CTZ). Patches were pulled from HEK293 cells transfected with cDNAs to express A1i/A2o and A1o/A2i and γ-8. Heteromerization was confirmed by calculating rectification index (RI, see below in C; only patches with RI > 0.7 were used). Mann-Whitney U test, ∗p < 0.05. (C) Subunit variant A2i is more effectively recruited by A1o. Heteromerization of A1i or A1o with A2i (R/G edited) expressed in HEK293T cells. cDNAs were cotransfected at an A1/A2 ratio of 4:1; a ratio limiting for A2 coassembly. I/V relationships (in the presence of 100 μM intracellular spermine) were quantified by determining the slope conductance (g) at +10mV and −40mV from the observed reversal potential and expressing these as a ratio, g+10 / g−40. RIs are summarized as box plots, numbers of patches for 1o/2i were n = 10 and were n = 12 for 1i/2i. Mann-Whitney U test, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Representative current traces of responses to 100 ms application of 3 mM L-Glu are shown above (current responses at −70mV, 0mV, and +50mV are shown). (D) A model of activity-dependent abundance of A1/A2 splice variant combinations in hippocampus based on the observed changes in CTZ efficacy and differential CTZ affinity of AMPAR flip variants.