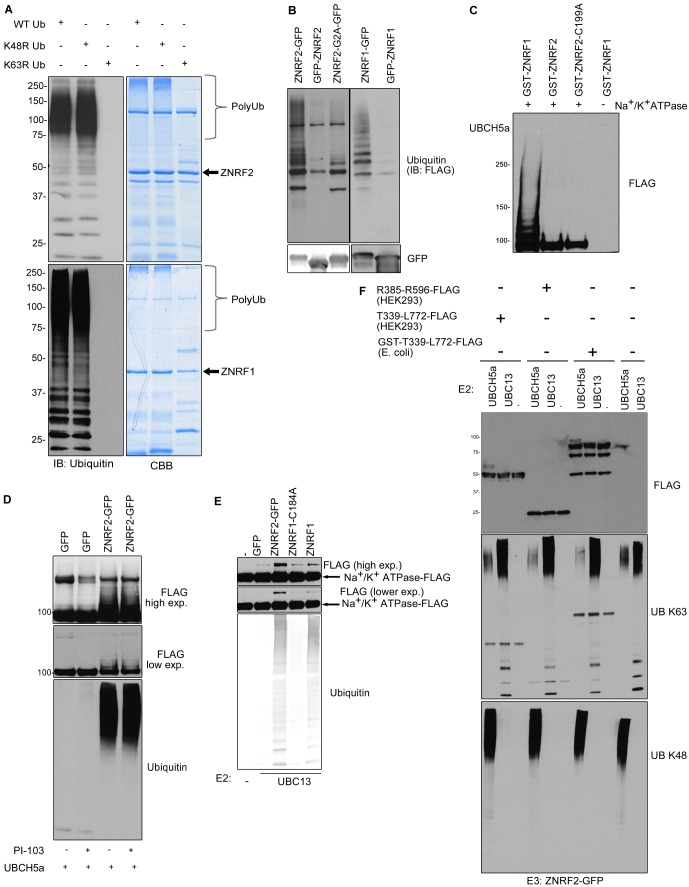
Fig. 7.
ZNRF1 can ubiquitylate Na+/K+ATPase α1 in vitro. (A) In vitro ubiquitylation reactions of ZNRF2 and ZNRF1 with (WT) ubiquitin, K48R ubiquitin or K63R ubiquitin were analyzed by western blotting (left) or Coomassie Blue staining (CBB, right). (B) The indicated proteins were immunoprecipitated from HEK293 cells and used for in vitro ubiquitylation reactions. (C) In vitro ubiquitylation reaction of FLAG-Na+/K+ATPase α1 purified from HEK293-Flp-In-TRex cells using GST-ZNRF1, GST-ZNRF2 or GST-ZNRF2-C199A. (D) As in C, except that the ZNRF2-GFP or GFP control was purified from HEK293-Flp-In-TRex cells treated with DMSO or PI-103 (1 µM, 30 min). UbcH5a was used as the E2. Reactions were analyzed by western blotting using anti-ubiquitin antibody (E) As in D, except Ubc13-Uev1a was used as the E2. The arrows indicate ubiquitylated FLAG-Na+/K+ATPase α1. Reactions were analyzed as in D. (F) The indicated fragments of Na+/K+ATPase α1 were purified either from HEK293 cells or E. coli and used for in vitro ubiquitylation reactions using either UbcH5a or Ubc13-Uev1a as the E2 and GFP-ZNRF2 as the E3. Reactions were analyzed by western blotting using K48- or K63-specific polyubiquitin chain antibodies.