Figure 2.
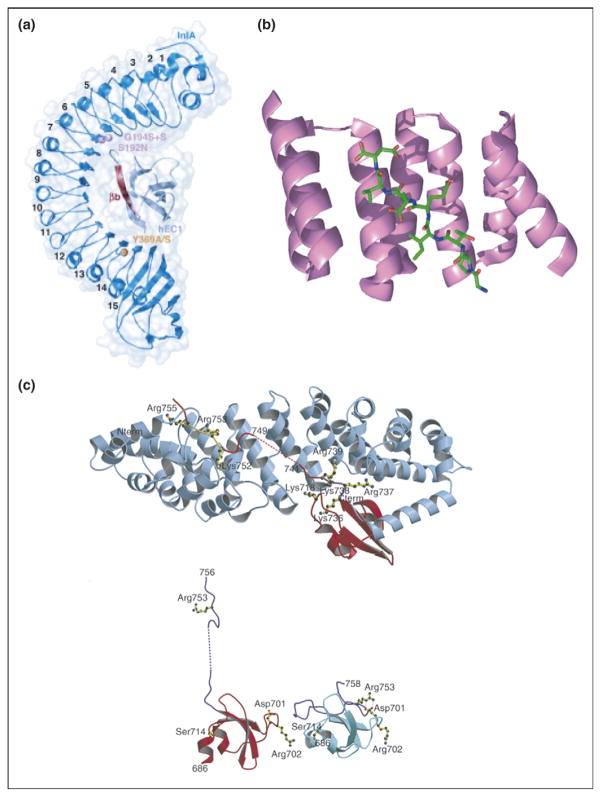
Repeat proteins bind to extended ligands. (a) Overall structure of internalin (InlA)/N-terminal domain of human E-cadherin (hEC1) complex shown to be in dark and light blue, respectively. The eight LRRs of InlA interact with a long, extended, β-strand of hEC1 [13••]. (b) Crystal structure of TPR1 domain of HOP in complex with the extended C-terminal peptide of Hsp70 bound in the concave face of the TPR domain. TPR1 domain is shown as a ribbon (purple) and the 8-mer C-terminal peptide of Hsp70 is shown as sticks (green) [37]. (c) (Top) Ribbon diagram showing C-terminal domain of influenza virus polymerase PB2 subunit (red) bound to human importin α5 (blue), comprising 10 armadillo repeats. (Bottom) Comparison of the PB2 domain structure in complexed (red) and free solution state (cyan) demonstrates unfolding of residues 736–759 (purple) upon binding to importin α5 [14••].