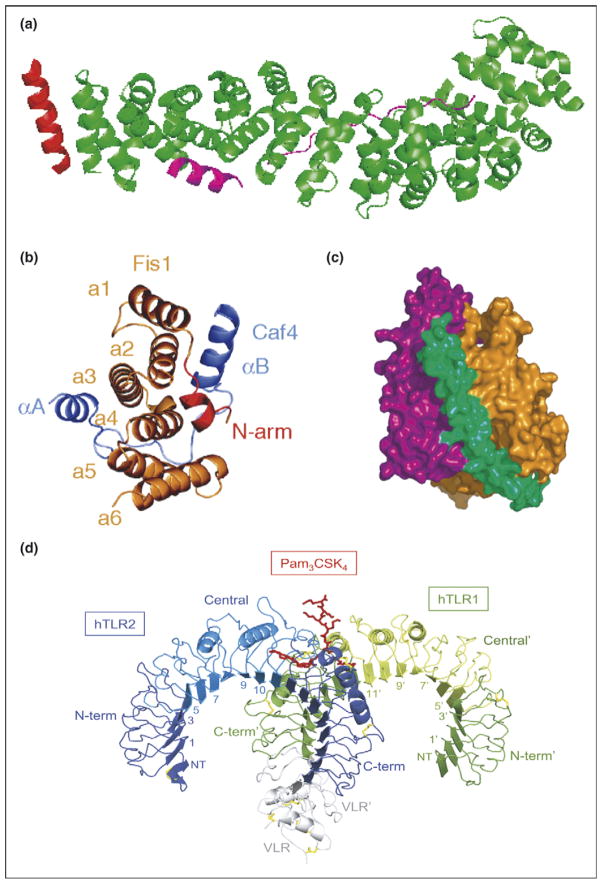
Figure 4.
Typical and atypical modes of binding. (a) Overall structure of the β-catenin/BCL9/Tcf-4 complex in green, magenta, and red, respectively. Packing of BCL9 against the groove formed between H2 and H3 of the N-terminal capping armadillo repeat to form a helical bundle illustrates atypical binding interface for armadillo repeat proteins [8]. (b) Fis1 TPR-Caf4 complex show a new two surfaces binding mode. Crystal structures of the TPR-like protein Fis1 in complex with Caf4 protein (PDB ID: 2pqr). The Fis1 N-terminal arm (red) remains packed against the original hydrophobic groove and stabilizes the B helix of Caf4 (purple), which packs against a second hydrophobic groove on the concave surface of Fis1. In addition to the B helix packed against the concave Fis1 surface, Caf4 (purple) uses the A helix and the intervening loop to bind the convex Fis1 surface [18]. (c) Molecular surface representation of CSL–Notch–Mastermind ternary complex. CSL (orange) and Notch (purple) interact to present composite surface for binding of Mastermind (green). (d) Overall structure of the human TLR1–TLR2–Pam3CSK4 complex. The TLR1 fragments and the TLR2 fragments are shown schematically in green and blue, respectively. The central domains are colored in light green or light blue, and the Pam3CSK4 lipopeptide in red. Disulfide bridges are represented as yellow lines. Domains belonging to the TLR1 hybrid proteins are labeled with apostrophes [21••].