FIGURE 2.
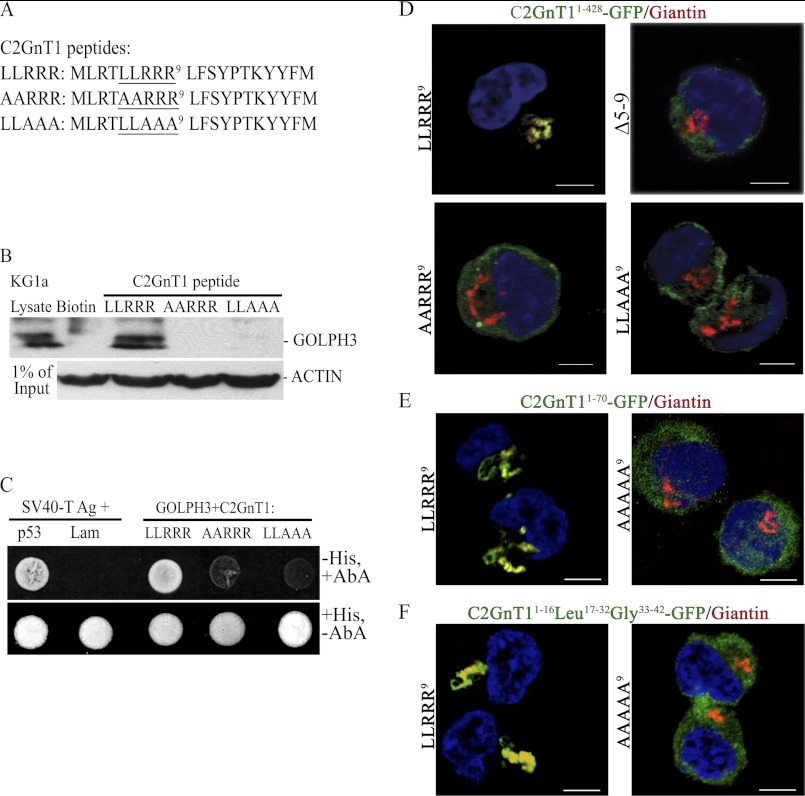
Identification of the amino acids in the C2GnT1 CT critical for binding to GOLPH3. A, sequences of the biotinylated C2GnT1 peptides used for the experiment; wild type (1–20) and mutants (Ala5,6 and Ala7–9). B, GOLPH3 Western blot analysis of the pulldown from KG1a lysates using biotin (control), biotinylated C2GnT1 1–20-aa peptide, and Ala5,6 and Ala7–9 mutants shown in A. C, forward yeast two-hybrid assay between Gal4(DBD)-C2GnT1(LLRRR9), Gal4(DBD)-C2GnT1 (AARRR9) or Gal4(DBD)-C2GnT1(LLAAA9), and Gal4(AD)-GOLPH3. Yeasts carrying the mutant plasmids did not grow (i.e. failure to interact with GOLPH3) in media lacking His but containing aureobasidin A. SV40 large T antigen and P53 are the positive controls and SV40 large T antigen and Lam are the negative controls. D, confocal fluorescence images of K562 cells transfected with various plasmid constructs showing differential Golgi localization of GFP: GFP is localized to the Golgi with the C2GnT1(1–428)-GFP construct but not the same construct with mutated CT such as deletion of amino acids 5–9, and mutation of AA6 or AAA9. E, GFP is localized to the Golgi using C2GnT11–70-GFP construct, but not the same construct with mutated CT (AAAAA9). E, GFP was localized to the Golgi using C2GnT1CT1–16-Leu17–32-Gly33–42-GFP construct but not the same construct with mutated CT (AAAAA9). Bar = 5 μm.