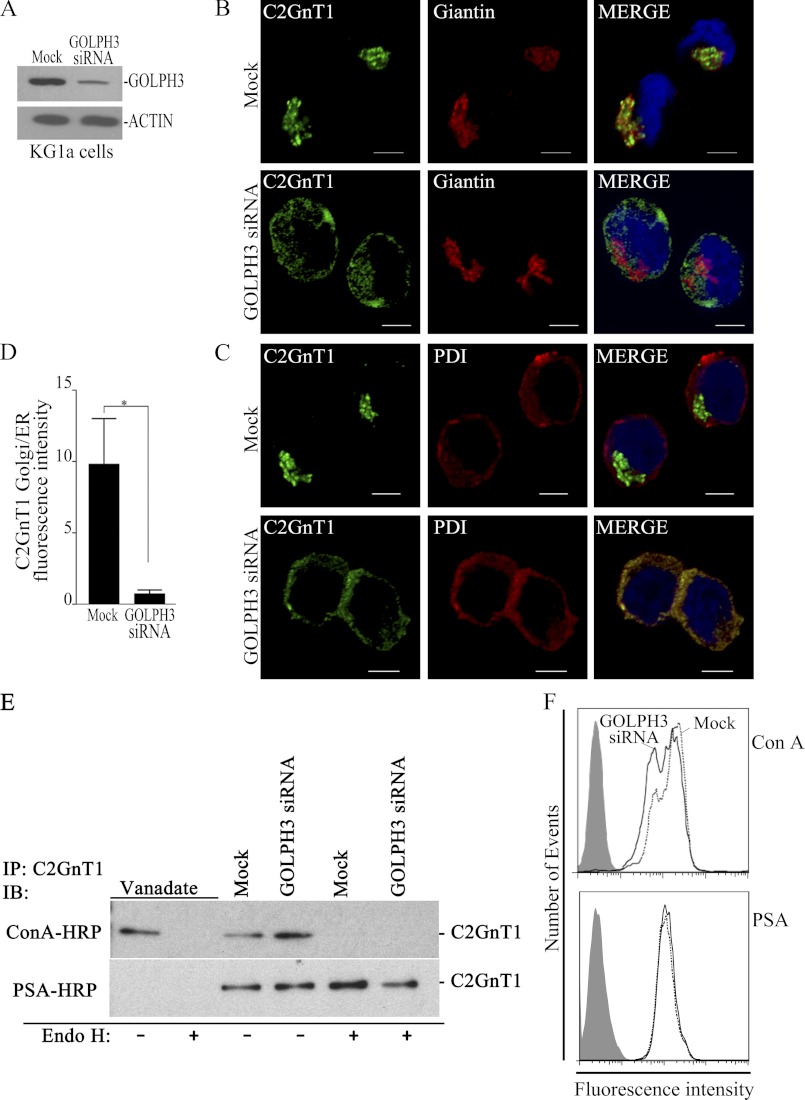
FIGURE 5.
GOLPH3 knockdown prevents Golgi localization of C2GnT1 without affecting the Golgi morphology, and analysis of the N-glycan types on C2GnT1 in KG1a cells treated with vanadate, water control, non-targeting or GOLPH3-specific siRNAs. A, GOLPH3 Western blot showing about 80–90% depletion of GOLPH3 in KG1a cells after transfection with GOLPH3 siRNAs as compared with cells transfected with non-targeting siRNAs (Mock). B and C, confocal fluorescence images of KG1a cells showing localization of C2GnT1 to the Golgi (Giantin) but distribution of C2GnT1 to the ER (protein-disulfide isomerase, PDI) after treatment with GOLPH3 siRNAs. D, quantification of the C2GnT1 fluorescence intensity in the ER relative to that of the Golgi in non-targeting or GOLPH3 siRNA-treated cells (n ≥ 25, bar = 5 μm). *, p < 0.01. E, ConA and PSA blots of the KG1a cell lysates with and without endoglycosidase H (Endo H) treatment. These KG1a cells have been treated with vanadate (inhibitor of ER-to-Golgi transport), water, non-targeting siRNAs (Mock), or GOLPH3 siRNAs. F, FACS analysis of KG1a cells after treated with fluorescein-labeled ConA or PSA lectin. Cells transfected with non-targeting siRNA (Mock), dotted line; or GOLPH3 siRNA, solid line. ConA binds high mannose-type N-glycans preferentially, PSA binds bi- and triantennary complex type N-glycans terminated with GlcNAc.