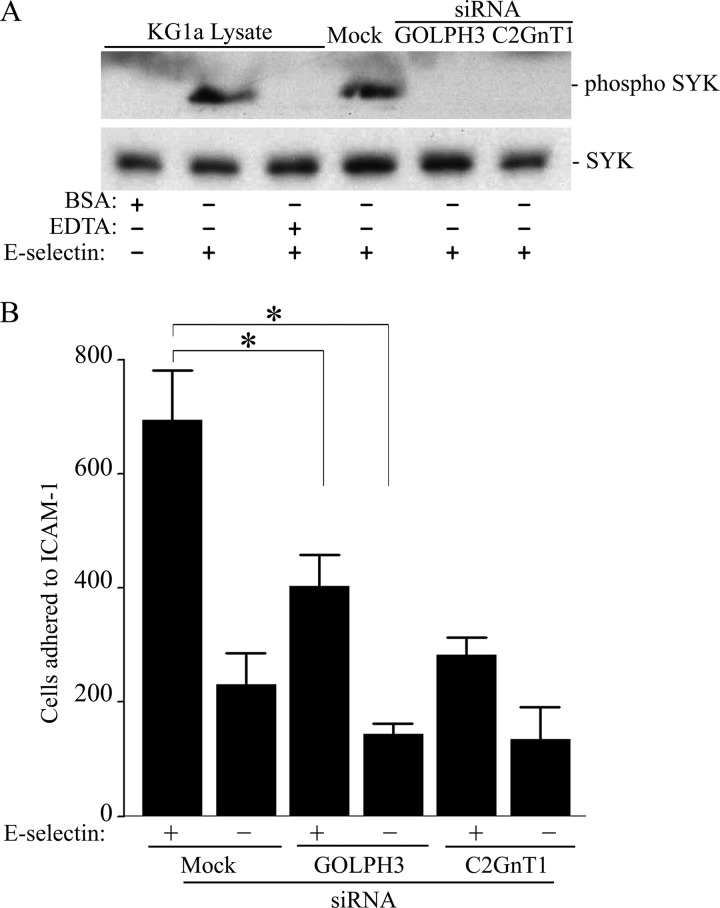
FIGURE 8.
GOLPH3 or C2GnT1 knockdown prevents activation of SYK and reduces the adhesion of E-selectin-treated KG1a cells to immobilized ICAM-1 under dynamic flow. A, EDTA, C2GnT1 siRNA, GOLPH3 siRNA, or non-targeting siRNA (mock)-treated cells were incubated with E-selectin for 20 min. Whole cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting for phosphorylated SYK. EDTA inhibits phosphorylation of SYK and BSA does not induce SYK phosphorylation. B, C2GnT1 siRNA, GOLPH3 siRNA, or non-targeting siRNA (mock)-treated cells (2.5 × 105 cells/ml) were incubated with E-selectin for 20 min before being perfused through a parallel plate flow chamber containing a coverslip coated with ICAM-1 at a constant wall shear stress of 1.0 dyne/cm2. Compared with mock treated cells, GOLPH3 or C2GnT1-depleted and E-selectin-activated KG1a cells exhibited a decrease in their adherence to immobilized ICAM-1 by 41.9 (694 ± 86 versus 403 ± 56, p < 0.05) and 59.2% (694 ± 86 versus 283 ± 30, p < 0.01), respectively.