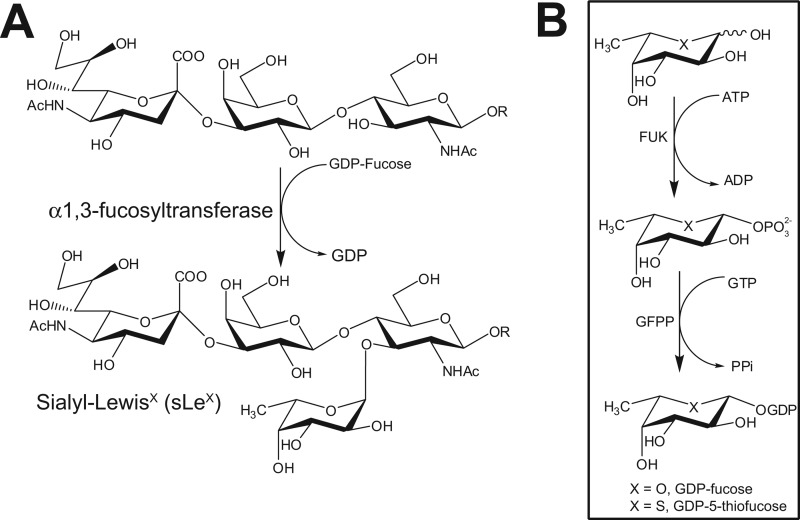
FIGURE 1.
The biosynthesis of sLeX and GDP-Fuc. A, the last and usually rate-limiting step in sLeX biosynthesis is the transfer of a Fuc residue onto a sialylated type 2 glycan precursor by FUTs. B, GDP-Fuc (X = O), the donor sugar for FUTs, is biosynthesized by cells de novo from GDP-mannose in a process requiring the sequential action of GDP-mannose 4,6-dehydratase (GMD) and GDP-keto-6-deoxymannose 3,5-epimerase (GDE). Alternatively, a salvage pathway converts free cytosolic fucose into GDP-Fuc upon its phorphorylation by fucose kinase (FUK) followed by the reversible condensation of fucose-1-phosphate with GTP by GDP-Fuc pyrophosphorylase (GFPP). The first steps of both pathways are subjected to feedback inhibition by GDP-Fuc. We hypothesize that 5T-Fuc (X = S) will be activated as GDP-5T-Fuc by the fucose salvage pathway and, if it is a poor substrate for FUTs, such as those that make sLeX, it may lead to the feedback inhibition of GDP-Fuc.