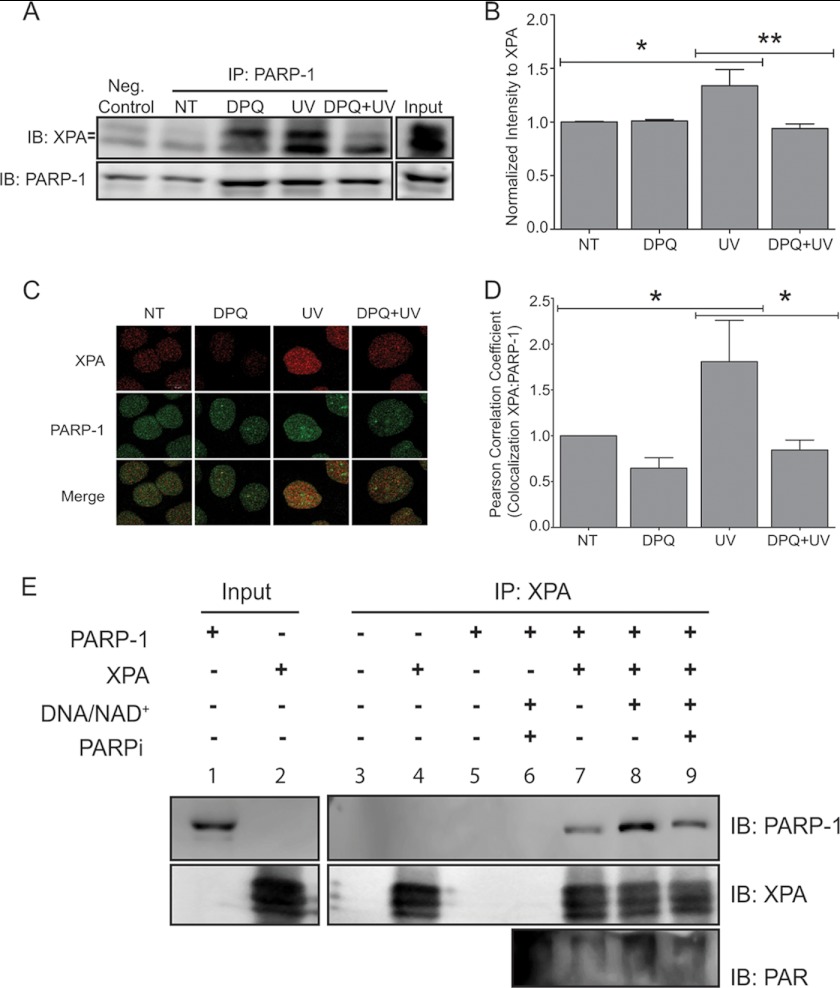
FIGURE 6.
Inhibition of PARP-1 activity leads to decreased association between PARP-1 and XPA. HaCaT cells were pre-exposed to a PARP inhibitor, DPQ, 30 min prior to UVR exposure. A, cells were collected 30 min post-UVR. Representative Western blot obtained from modified chromatin immunoprecipitation method (ChIP-on-Western). PARP-1 was immunoprecipitated (IP) from chromatin complexes. The membranes were immunoblotted (IB) for XPA and subsequently immunoblotted for PARP-1 as confirmation for immunoprecipitation. B, quantification of Western blot by densitometry. The data are presented as the means ± S.E., n = 3. C, HaCaT cells were pre-exposed to a PARP inhibitor, DPQ, 30 min prior to UVR exposure and cells were fixed 1 h post-UVR. Dual staining with antibodies against XPA (red) and PARP-1 (green) was performed to assess the amount of co-localization (merge, yellow). D, graph representing co-localization between XPA and PARP-1. The percentage of co-localization was determined using Pearson's correlation coefficient. The data are presented as the means ± S.E., n = 3. E, purified PARP-1 and His-XPA were incubated alone (lane 7), with activated PARP-1 (addition of activated DNA and NAD+, lane 8), or in the presence of the PARP inhibitor AG-014699 (lane 9). Following the various treatments, His-XPA was pulled down (IP) from each sample using cobalt-conjugated magnetic beads. Following pulldown, the membranes were subsequently immunoblotted (IB) for PARP-1, XPA, and PAR, NT=untreated. n = 3. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. Scale bar, 10 μm.