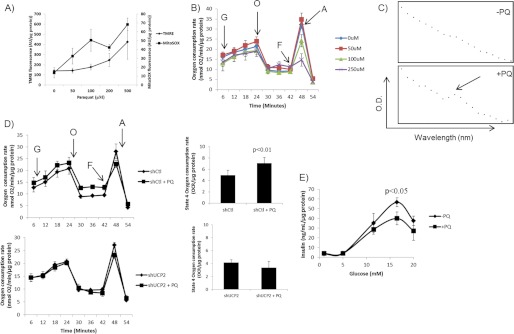
FIGURE 6.
Matrix ROS activates leak through UCP2 that impedes GSIS. To simulate production of superoxide in the matrix without inhibiting the respiratory complexes, Min6 cells were incubated for 18 h with paraquat (PQ). A, PQ-mediated increases in matrix ROS are dose-dependent. Cells were pre-loaded with either MitoSOX (20 μm) or TMRE (10 nm) and energized for 1 h with 25 mm glucose. Fluorescent signals were then detected and compared to determine whether PQ generates superoxide in the matrix and whether PQ uptake has an effect on mitochondrial membrane potential. Data were normalized to total protein per well. B, impact of PQ on Min6 mitochondrial bioenergetics. Following an assessment of resting respiration, respiration rates in cells treated to PQ (0–250 μm) were tested following exposure to glucose (G; 25 mm), oligomycin (O; 0.13 μg/ml), FCCP (F; 2 μm), and antimycin A (A; 2 μm). Data were normalized to total protein per well. n = 4, mean ± S.E. C, PQ accumulates in mitochondria. Following exposure of Min6 cells to 0 or 50 μm PQ, mitochondria were isolated, lysed, and treated with dithionite. PQ was detected by UV-visible scan from 500 to 700 nm. D, PQ activates UCP2 proton leak. Min6 cells transduced with either short hairpin control (shCtl) or UCP2 (shUCP2) lentiviral particles and treated with or without PQ (50 μm) were sequentially treated with glucose (G; 25 mm), oligomycin (O; 0.13 μg/ml), FCCP (F; 2 μm), and antimycin A (A; 2 μm). Impact of PQ on UCP2-dependent proton leak is summarized to the right of the bioenergetic data. All data were normalized to total protein per well. n = 4, mean ± S.D. Student's t test. E, PQ impedes GSIS. Min6 cells were starved and then treated with different amounts of glucose (1–20 mm) for 1 h. Insulin levels in the incubation medium were normalized to total protein amounts/well. n = 4, mean ± S.E. Student's t test.