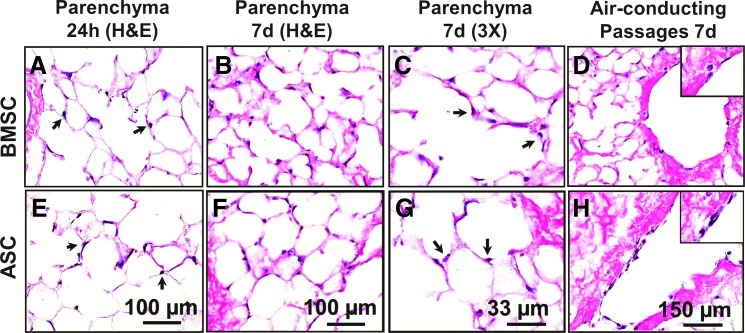
FIG. 5.
Initial seeding of rhesus BMSC and ASC within the acellular lung matrix shows adhesion and elongation in culture. (A–H) Rhesus BMSC and ASC seeded into decellularized macaque lung scaffolds attach to the matrix and persist in culture. (A, E) After 24 h (24h), cells were observed attaching to the matrix by H&E stain (arrows). (B, F) At 7 days (7d), cells persisted in the matrix and maintained an elongated phenotype. (C, G) High magnification (30×) images of H&E stained sections from 7d samples showed dark (hematoxylin-stained) nuclei and lighter (eosinophilic) cytoplasmic projections (arrows). (D, H) In addition to adherence to the alveolar septal matrix, both BMSC and ASC adhere to air-conducting passages. Images acquired at 100× or 300× magnification as indicated; insets represent 300× magnification. BMSC, bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell; ASC, adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/tea