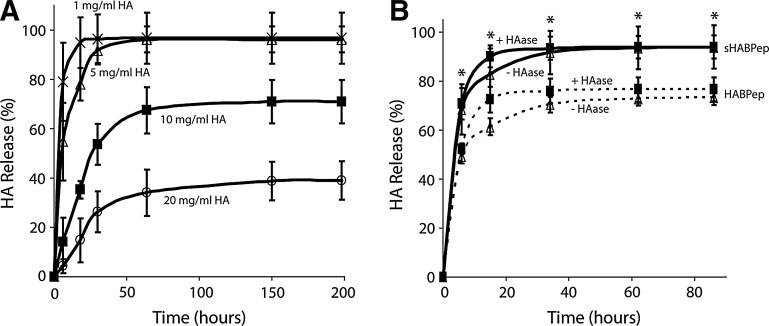
FIG. 1.
Hyaluronic acid (HA)-interacting hydrogels increase retention of HA. (A) Release of HA from control noninteracting hydrogels was assessed at various HA loadings to determine the effects of nonspecific interactions between HA and poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate. At steady state, HA loading concentrations of 1 mg/mL and 5 mg/mL were fully released from the hydrogel. (B) Specific interactions between HA and HABPep-functionalized hydrogels were assessed at 5 mg/mL HA loading. HABPep was shown to significantly decrease HA release at steady state (*denotes significance between HABPep and scrambled controls at each time point, p<0.05). Addition of hyaluronidase increased the kinetics of release, but not the equilibrium behavior. HABPep, HA-binding peptide.