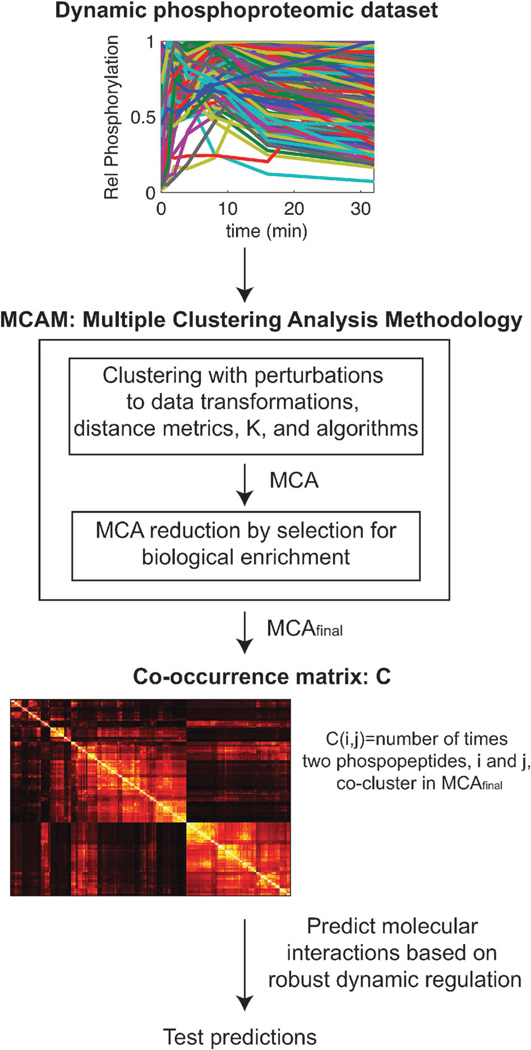
Fig. 1.
Methodology for predicting protein macromolecular interactions through the robust co-regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation dynamics. A quantitative, dynamic, global dataset of phosphorylation is subjected to MCAM, which combinatorially applies a variety of transforms, distance metrics, algorithms, and cluster numbers (K) to produce an ensemble of clustering solutions, termed MCA for Multiple Clustering Analysis. The initial MCA is then pruned to remove those sets that yield little meaningful biological insight according to statistical significance of enrichment for biological terms such as Gene Ontology annotations, protein domains, and predictions of the responsible kinase. This pruned set, MCAfinal, is then analyzed for robust dynamic regulation by considering the number of times any pair of phosphopeptides co-cluster in the full set. Robust and interesting results can then be tested for accuracy regarding dynamic molecular interaction in the original conditions the dataset was collected under.