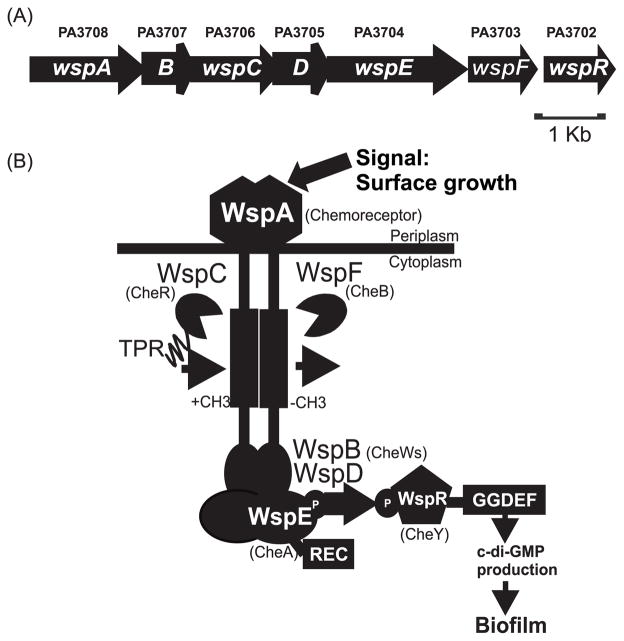
Fig. 1. Schematic model of the Wsp system.
(A) Genetic organization of the wsp locus in PAO1. (B) Model of the Wsp protein complex. The chemotaxis counterparts of the Wsp proteins are indicated in parentheses. WspA, the receptor, detects a signal associated with growth on a surface. WspB and WspD are CheW-like proteins. WspE is a CheA-like histidine kinase with an additional receiver domain (REC) at the C-terminus. WspR is a REC-GGDEF domain protein that has diguanylate cyclase activity. WspC is a predicted CheR-like methyltransferase with a C-terminal tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domain and WspF is a predicted CheB-like methylesterase. In our model, detection of surface growth by WspA results in phosphorylation of WspR. Phosphorylated WspR synthesizes c-di-GMP, which triggers biofilm formation.