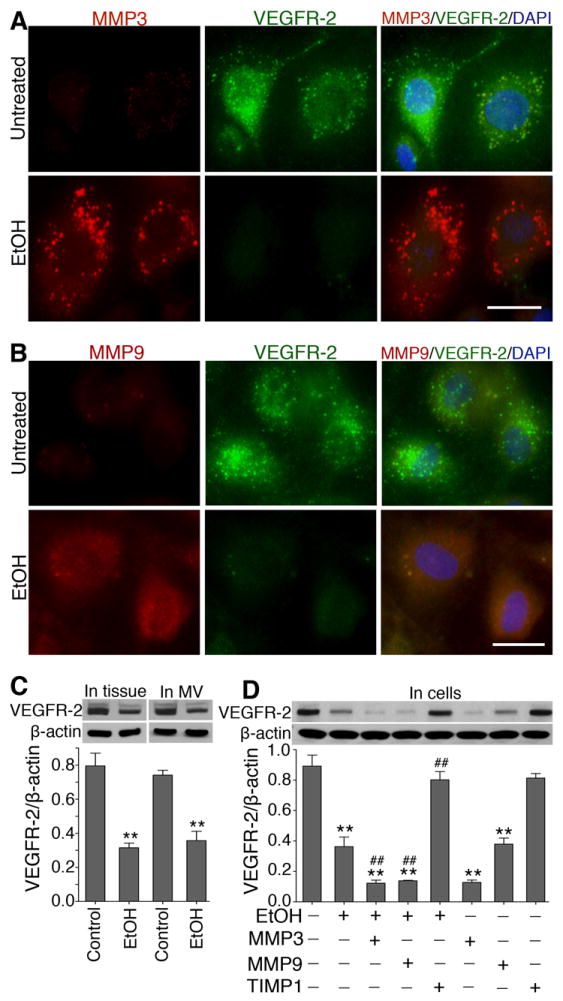
Figure 2. Activation of MMP-3/9 causes BBB leakiness.
A, Kinetic profile of the trans-endothelial electrical resistance (TEER) across the BBB following EtOH, MMP-3/9, TIMP1, VEGF-A or Ki8751 treatment. After maintaining a stable resistance for 2 hr, TEER was monitored at 400 Hz with 10 min intervals. Reproducible results were obtained in 3 individual experiments. B, In vivo permeability of Evans Blue (EB, 5 μM) and Sodium fluorescein (Na-Fl, 5 μM) across the BBB (n=5). C, Migration of monocytes across the in vitro model of BBB after treatment of various test compounds as shown in figure. Data are expressed as fold difference from untreated cells. D, Effects of EtOH (50 mM), VEGF-A (100 ng/mL), Ki8751 (10 μM), EtOH+VEGF-A or EtOH+Ki8751 on occludin, claudin-5 and ZO-1 levels in hBECs after 24 hr exposure (Western blotting). E, Fluo-3 labeled macrophage adhesion/migration in brain capillary following infusion of cells into the common carotid artery. F, Immunofluorescent staining of CD68 (green) and von Willibrand factor (green) merged with DAPI (blue) in microvessel of brain tissue section. Scale bar indicates 5 μm in all panels. *p<0.05; **p<0.01 vs untreated or control in A, B and C; #p<0.05; ##p<0.01 vs EtOH (second bar) in C.
