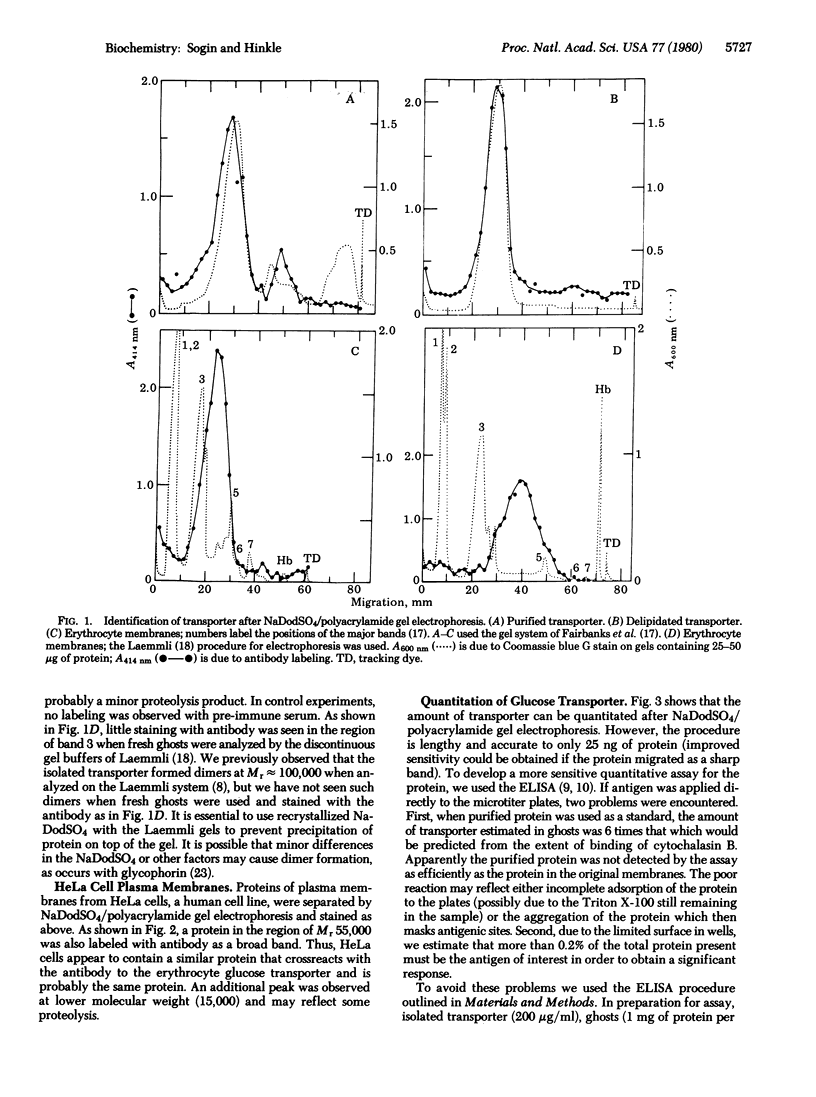
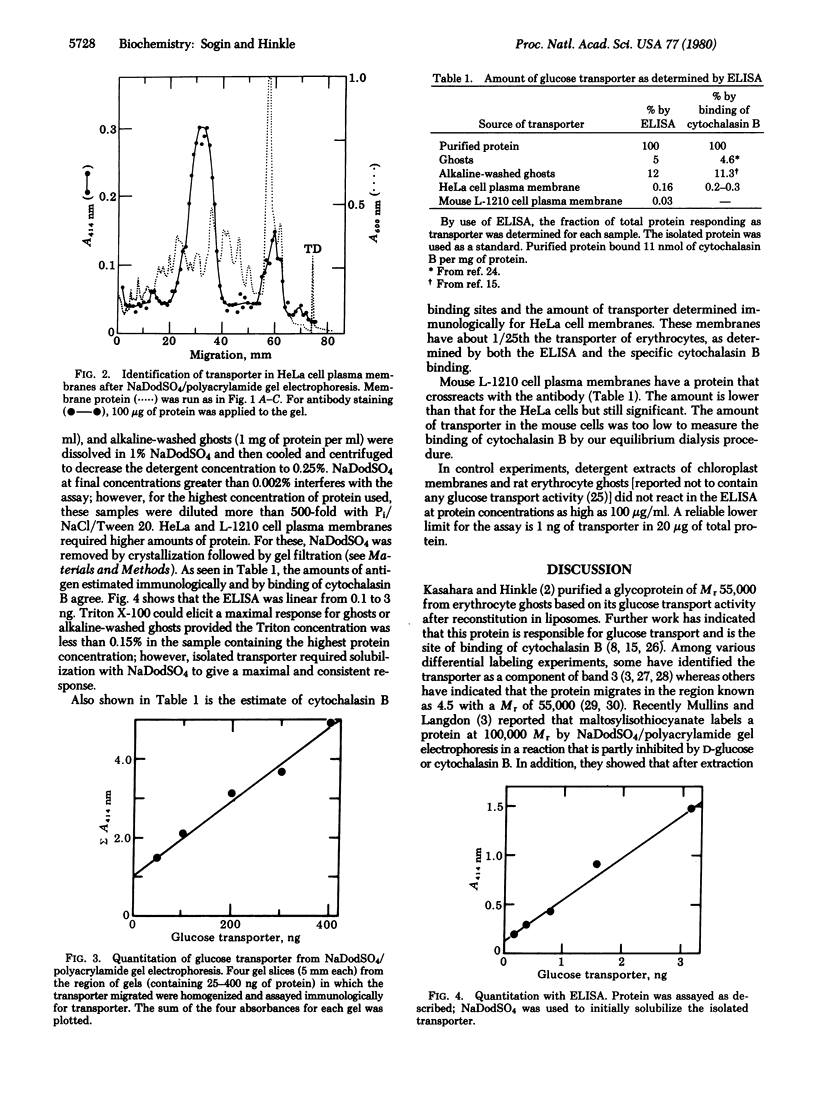
Abstract
A rabbit antibody against the human erythrocyte glucose transporter was purified by affinity chromatography and used to determine the distribution of transporter on polyacrylamide gels after electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate. Fresh erythrocyte ghosts showed transporter only at the broad 55,000 Mr band, as did the isolated transporter. HeLa cell plasma membranes showed a similar band of crossreacting material at Mr 55,000. The amount of crossreacting material in human erythrocyte ghosts and in plasma membranes from human HeLa cells and mouse L-1210 cells was determined in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay which gave results consistent with the extent of glucose-reversible binding of cytochalasin B.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin S. A., Baldwin J. M., Gorga F. R., Lienhard G. E. Purification of the cytochalasin B binding component of the human erythrocyte monosaccharide transport system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 23;552(1):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90257-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batt E. R., Abbott R. E., Schachter D. Impermeant maleimides. Identification of an exofacial component of the human erythrocyte hexose transport mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7184–7190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker R., Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of the Semliki Forest virus membrane with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Biochemistry. 1975 May 6;14(9):1835–1841. doi: 10.1021/bi00680a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs R. E., Bardsley W. G. The steady-state kinetics of peroxidase with 2,2'-azino-di-(3-ethyl-benzthiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) as chromogen. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;145(1):93–103. doi: 10.1042/bj1450093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Molecular basis of insulin action. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:359–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka M. Transport of sugars in tumor cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 29;355(1):77–104. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(74)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung C. Y., Carlson L. M. Glucose transport carrier in human erythrocyte membranes. Dinitrophenylation of a membrane component modified by D-glucose. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3217–3220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung C. Y., Rampal A. L. Cytochalasin B binding sites and glucose transport carrier in human erythrocyte ghosts. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5456–5463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara M., Hinkle P. C. Reconstitution and purification of the D-glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7384–7390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara M., Hinkle P. C. Reconstitution of D-glucose transport catalyzed by a protein fraction from human erythrocytes in sonicated liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):396–400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever J. E. Active amino acid transport in plasma membrane vesicles from Simian virus 40-transformed mouse fibroblasts. Characteristics of electrochemical Na+ gradient-stimulated uptake. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1990–1997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lienhard G. E., Gorga F. R., Orasky J. E., Jr, Zoccoli M. A. Monosaccharide transport system of the human erythrocyte. Identification of the cytochalasin B binding component. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 1;16(22):4921–4926. doi: 10.1021/bi00641a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins R. E., Langdon R. G. Maltosyl isothiocyanate: an affinity label for the glucose transporter of the human erythrocyte membrane. 2. Identification of the transporter. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1205–1212. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Richey D. P. Transport of nucleosides, nucleic acid bases, choline and glucose by animal cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 16;344(3-4):263–305. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(74)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERG T., VESTERGAARD-BOGIND B., WILBRANDT W. Modellversuche zur Trägerhypothese von Zuckertransporten. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1956;14(3):334–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S. N., Amos H. Insulin stimulation of glucose entry in chick fibroblasts and HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jul 2;53(1):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg M., Marchesi V. T. The anomalous electrophoretic behavior of the major sialoglycoprotein from the human erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):95–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin D. C., Hinkle P. C. Characterization of the glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. J Supramol Struct. 1978;8(4):447–453. doi: 10.1002/jss.400080407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarone G., Hamasaki N., Fukuda M., Marchesi V. T. Proteolytic degradation of human erythrocyte band 3 by membrane-associated protease activity. J Membr Biol. 1979 Jun 29;48(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01869253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverna R. D., Langdon R. G. D-glucosyl isothiocyanate, an affinity label for the glucose transport proteins of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 18;54(2):593–599. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bartlett A., Bidwell D. E. Enzyme immunoassays with special reference to ELISA techniques. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jun;31(6):507–520. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.6.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weliky N., Weetall H. H. Studies of antigen-antibody interaction on some specific solid adsorbents derived from cellulose. Immunochemistry. 1972 Oct;9(10):967–978. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


