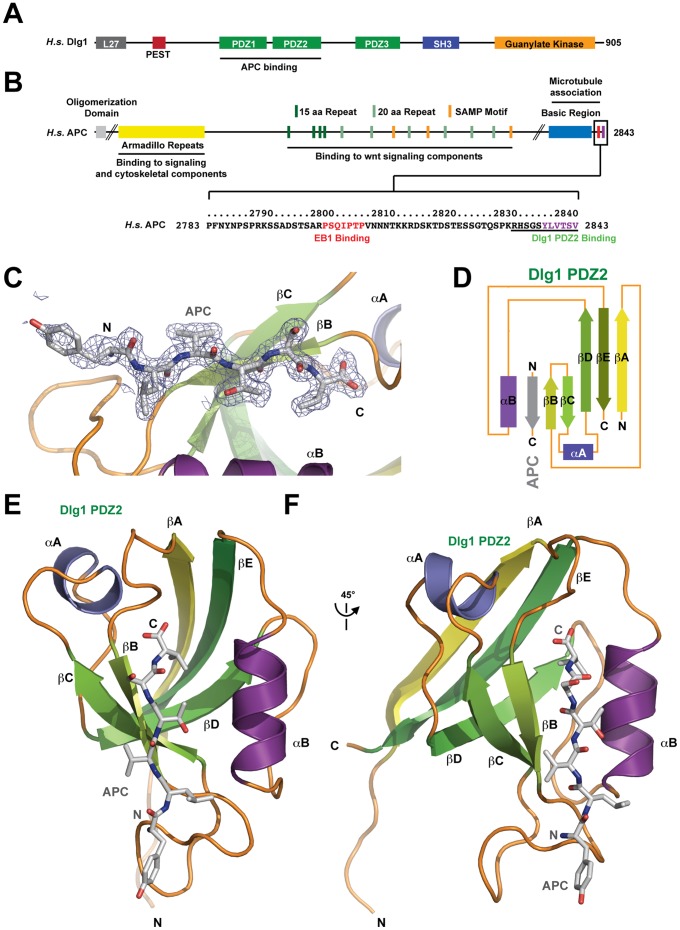
Figure 1. Overall structure of the Dlg1 PDZ2-APC complex.
A) Domain arrangement of H.s. Dlg1. Shown is the L27 domain (grey), PEST motif (red), PDZ domains 1–3 (green), SH3 (dark blue), and guanylate kinase domain (orange). B) Domain arrangement of H.s. APC. Shown is the oligomerization domain, the armadillo repeat domain, 15 and 20 aa repeat sequences used in β-catenin binding, SAMP motifs used for axin binding, a basic region with microtubule binding activity, and C-terminal EB1 and Dlg1 binding sites. The C-terminal region is boxed and corresponding sequence shown below. Highlighted in red is the SxIP motif and flanking residues that bind the microtubule plus end tracking protein EB1. The C-terminal six residues that bind Dlg1 PDZ2 are highlighted in purple. The APC peptide synthesized in this study is indicated by an underline. C) Zoom view of the APC peptide bound to hDlg PDZ2. Final, refined 2Fo-Fc electron density around the APC peptide is displayed and contoured at 1.0 σ. D) 2° structure topology of Dlg1 PDZ2 complexed with the C-terminal APC β-strand (grey), which runs anti-parallel to Dlg1 PDZ2 βB and parallel to αB. E) Ribbon diagram of Dlg1 PDZ2 complexed with the APC C-terminal six residues shown in stick format. F) Structure shown in E, rotated 45° about the y-axis. The Dlg β-strands are colored in a yellow to dark green continuum, loop regions are colored orange, helices αA and αB are colored slate and purple respectively, and the APC peptide is colored grey (C–F).