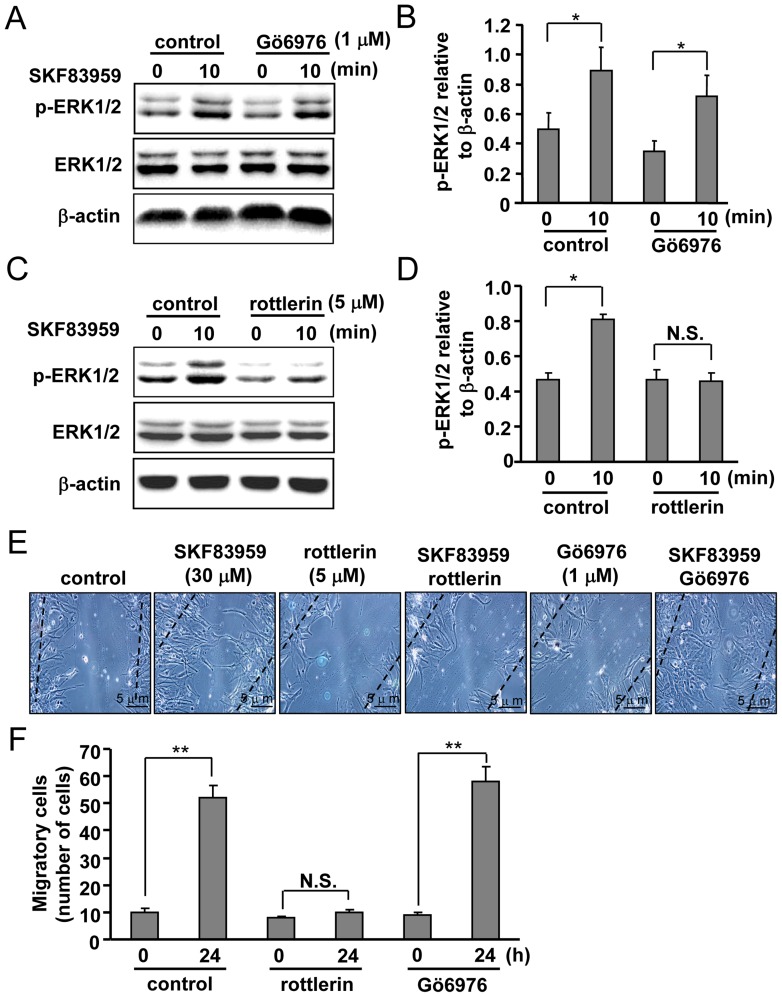
Figure 6. Roles of PKCδ and PKCα in SKF83959-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation.
(A) Effects of the PKCα inhibitor Gö6976 (1 µM, 30 min) on SKF83959 (30 µM, 10 min)-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation. (B) Quantitative analysis of pretreatment with 1 µM Gö6976 on SKF83959-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation (Mean ± S.E., n = 3, *P < 0.05, 10 min vs. 0 min). (C) Effects of PKCδ inhibitor rottlerin (5 µM, 30 min) on SKF83959 (30 µM, 10 min)-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation. (D) Quantitative analysis of pretreatment with rottlerin on SKF83959-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation (Mean ± S.E., n = 3, *P < 0.05, 10 min vs. 0 min). N.S.: no significance. (E) Respective roles of rottlerin (middle, 5 µM, 30 min) and Gö6976 (right, 1 µM, 30 min) in SKF83959 (30 µM, 24 h)-induced migration of astrocytes. Bar: 5 µm. (F) Statistical analysis of respective pretreatment with rottlerin (middle) and Gö6976 (right) on SKF83959-induced migration of astrocytes (Mean ± S.E., n = 3, **P < 0.01, 24 h vs. 0 h). N.S.: no significance.