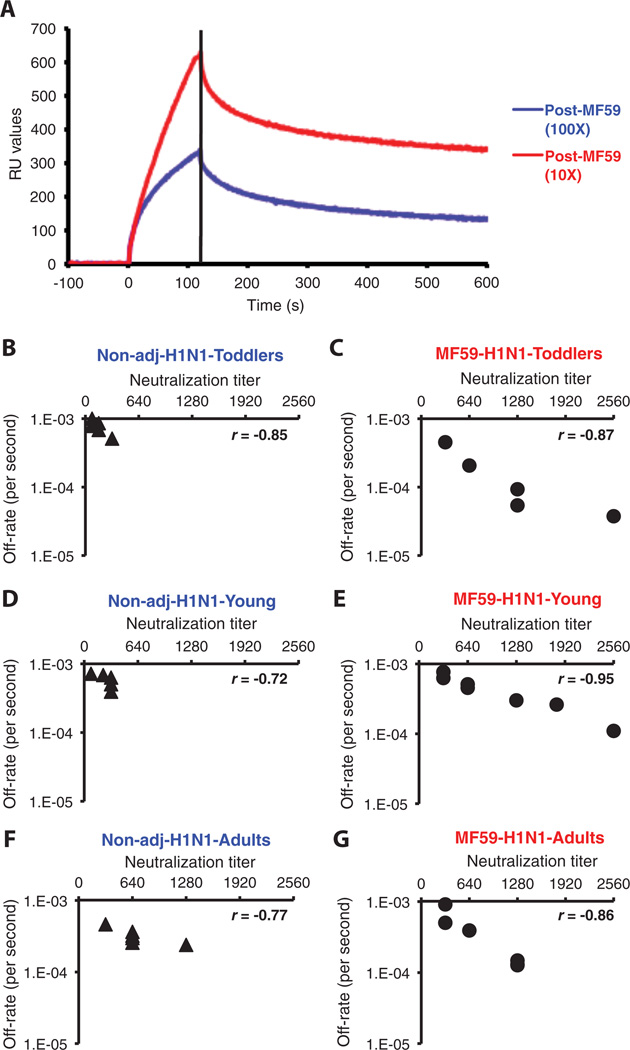
Fig. 6.
Affinity measurements and correlation between in vitro neutralizing capacity and off-rate constant in human sera after immunization with an MF59-adjuvanted and unadjuvanted H1N1 subunit vaccine in different age groups. (A) Antibody avidity measurements in polyclonal serum by off-rate constants with SPR. Antibody off-rate constants that describe the stability of the complex, which is the fraction of complexes that decays per second, were determined directly from the serum-plasma sample interaction with rHA1 protein using SPR in the dissociation phase. For accurate measurements, parallel lines in the dissociation phase for the 10- and 100-fold dilution for each post-vaccination human sera were required. The off-rate constants were determined from two independent SPR runs. (B to G) SPR analysis of post-vaccinated human sera with MF59-adjuvanted (C, E, and G) or unadjuvanted SOIV-H1N1 (B, D, and F) vaccine from three age groups of the vaccine trial was performed with properly folded SOIV-H1N1 HA1 (A/California/07/2009) (21). Serum antibody off-rate constants and serum-neutralizing antibody titers for different individual vaccinees (each symbol is one individual) were determined as described in Materials and Methods. Neutralizing titer is expressed as standardized end-point neutralizing antibody titer of post-H1N1 vaccine human sera. Antibody off-rate constants of human sera after vaccination with MF59-adjuvanted or unadjuvanted SOIV-H1N1 vaccine correlated with their in vitro neutralizing capacity. Correlation statistics of the affinity measurement and off-rate constants of the human sera between MF59-adjuvanted and unadjuvanted vaccine groups were statistically significant only for the toddlers’ samples (12 to 35 months) and young children (3 to 8 years), with P < 0.05 (t test).