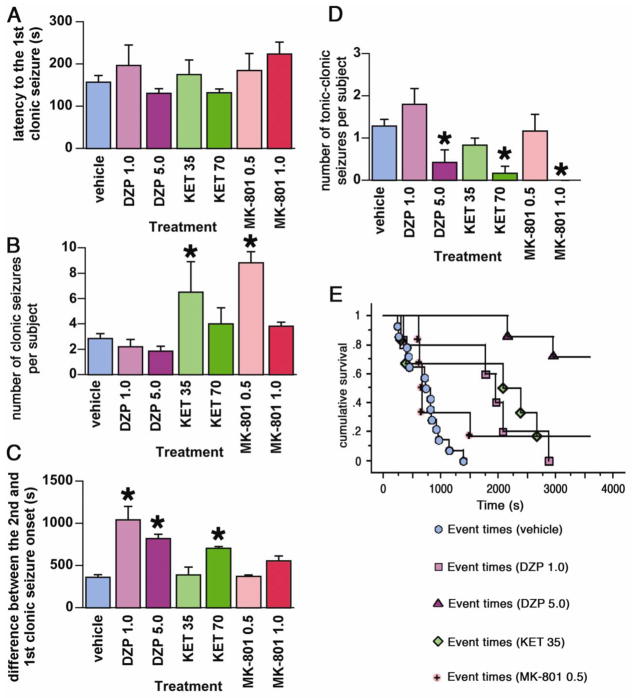
Figure 2. Post-treatment effects of DZP, KET, and MK-801 on TMDT syndrome.
2A. Latency to onset of the first clonic seizures (mean ± S.E.M.) induced by TMDT plus post-treatment with one of the following: vehicle; DZP 1.0 or 5.0 mg/kg, KET 35 or 70 mg/kg, MK-801 0.5 or 1.0 mg/kg. All treatments were administered immediately after the first clonic seizure. There was no statistically significant difference in TMDT clonic seizure onset prior to drug post-treatment.
2B. Number of clonic seizures (mean ± S.E.M.) in mice injected with 0.4 mg/kg TMDT and one of the postreatments. KET 35 mg/kg and MK-801 0.5 mg/kg increased the number of clonic seizures (Kruskal-Wallis test; *p<0.05).
2C. Mean ± S.E.M. time difference between the onset of the first and second clonic seizure. DZP (both 1.0 and 5.0 mg/kg) and KET (70 mg/kg) significantly extended this time difference compared to vehicle-injected controls (*p<0.05; ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett’s test).
2D. Number of tonic-clonic seizures (mean ± S.E.M.) in mice injected with 0.4 mg/kg TMDT for each post-treatment. Higher doses of DZP (5.0 mg/kg), KET (70 mg/kg), and MK-801 (1.0 mg/kg) significantly decreased number of tonic-clonic seizures occurring during the observation period compared to vehicle (*p<0.05; Kruskal-Wallis test).
2E. Non-parametric survival analysis of the latency to onset of tonic-clonic seizures in all post-treatment groups in which tonic clonic seizures occurred.