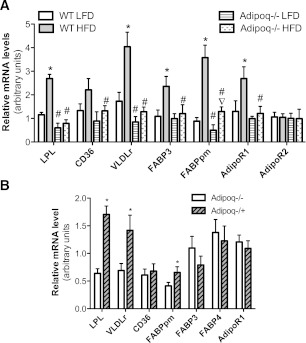
FIG. 4.
Adiponectin and maternal obesity enhanced expression of genes that facilitate placental FA transport. Placentas were collected by Cesarean section at e17.5. mRNA levels were determined by real-time PCR. Maternal obesity was induced by HF-diet feeding using WT and Adipoq−/− dams and breeding scheme 1 (A) (see detail in the Research Design and Methods section and Supplementary Fig. 1A). The breeding scheme 2 was used to produce Adipoq−/+ or Adipoq−/− fetuses, whereas maternal adiponectin was null (B) (Supplementary Fig. 1B). These dams were fed with chow (B). Elevated mRNA levels of placental LPL, VLDLr, FABP3, and FABPpm and AdipoR1 were detected in placentas from obese WT dams (A, designated as WT HFD). However, the differences were diminished, except for FABPpm, in placentas of HFD- and LFD-fed Adipoq−/− dams (A, designated as Adipoq−/− HFD and Adipoq−/− LFD). Elevated mRNA levels of LPL, VLDLr, and FABPpm were observed in placentas of Adipoq−/+ fetuses, whereas the dams were Adipoq−/− (B). *P < 0.05 vs. WT LFD (A) or Adipoq−/− fetuses (B); #P < 0.05 vs. WT LFD or WT HFD (A); ▽P < 0.05 vs. Adipoq−/− LFD. HFD, HF diet; LFD, LF diet; n = 12.