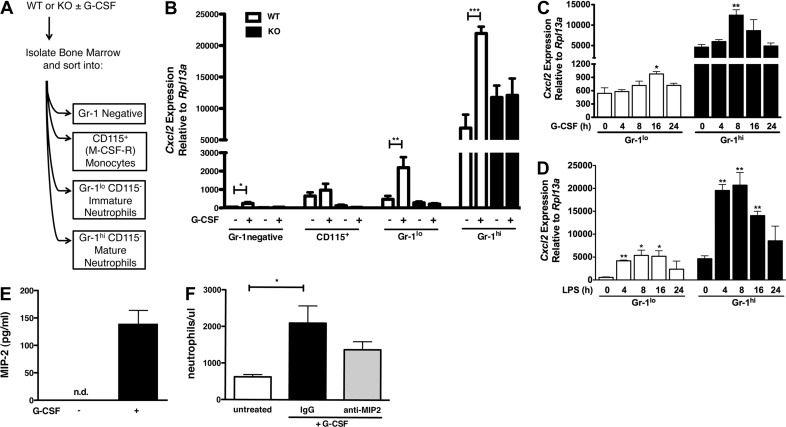
Figure 1. G-CSF stimulates Cxcl2 and MIP-2 expression in Gr-1hi mature neutrophils.
(A) Schematic diagram of the cell-sorting strategy. (B) WT (white bars) and Stat3-deficient [knockout (KO); black bars] mice were treated with G-CSF (250 μg/kg) or left untreated. Bone marrow cells were harvested after 24 h, purified by cell sorting as indicated, and analyzed by qPCR for expression of Cxcl2. Shown are mean expression levels relative to the housekeeping gene Rpl13a ± sem (n≥3). (C and D) WT Gr-1lo immature and Gr-1hi mature neutrophils were purified by cell sorting and cultured with 25 ng/ml G-CSF (C) or 0.1 μg/ml LPS (D) for 0, 4, 8, 16, or 24 h. Cxcl2 mRNA amounts were determined by qPCR as indicated in B (n=3). (E) WT Gr-1hi mature neutrophils were purified by cell sorting and cultured in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 25 ng/ml G-CSF for 24 h, as indicated. MIP-2 expression was analyzed in culture supernatants by ELISA. Results show mean values ± sem (n≥3). (F) WT C57BI6 mice were treated with 20 μg anti-MIP-2 antibody (gray bar), IgG isotype control (black bar), or left untreated (white bar). After 30 min, mice were treated with G-CSF as indicated in B. Results show mean neutrophil levels/ml blood ± sem, determined 6 h after G-CSF treatment (n≥3). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.