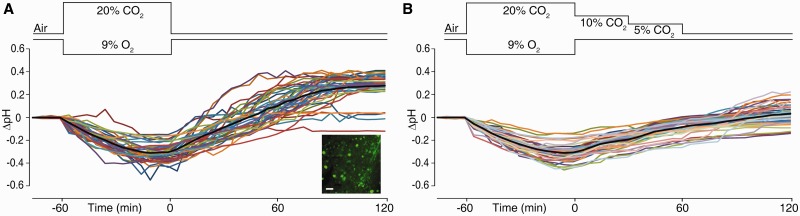
Figure 1.
An intraneuronal alkalosis is triggered after asphyxia and suppressed by graded restoration of normocapnia. The experimental changes in inhaled CO2 and O2 are schematically shown above the recordings. (A) Two-photon in vivo measurements of intracellular pH changes (mean ΔpH indicated by black line) in 40 layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons shown in colour from five Day 6–7 rat pups. Inset shows BCECF-loaded neurons. Scale bar = 20 µm. (B) Intracellular ΔpH in 41 neurons from five rat pups in the graded restoration of normocapnia paradigm.