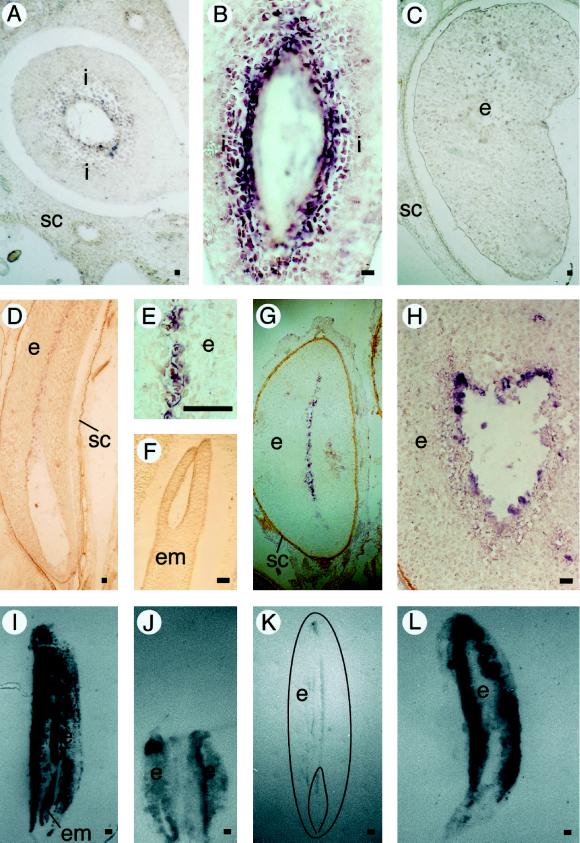
Figure 5.
EP3 gene expression in seeds. A, Cross-section of a fruit 7 DAP. B, Longitudinal section of a fruit 7 DAP. C, Cross-section of a fruit 20 DAP. D, Longitudinal section of a mature seed. E, Longitudinal section of a mature seed. F, Zygotic embryo in a longitudinal section of a mature seed. G, Transverse section of a seed that soaked in water for 60 h. H, Transverse section of a seed that soaked in water for 60 h. In the immunolocalizations, the presence of EP3 proteins is visible as a dark precipitate. Bar = 100 μm. I, Control tissue print of a mature seed stained with amido black. J, Immunolocalization of EP3 on a tissue print of a fruit containing two developing seeds 20 DAP. K, Immunolocalization of EP3 on a tissue print of a mature seed (a drawing of the printed seed is superimposed on the picture). L, Immunolocalization of EP3 on a tissue print of a seed that soaked in water for 60 h. Plant material was analyzed by in situ hybridization on sectioned carrot seeds with antisense EP3 RNA probes (A–H). Light microscopy (coupled to Nomarski optics for A–E) was used for visualization of the purple precipitate (the use of Nomarski optics resulted in a change from purple to brown in D). Immunolocalization of the EP3 protein was done by tissue printing followed by immunostaining (I–L). i, Integuments surrounding the developing embryo and endosperm; SC, seed coat; e, endosperm; em, embryo. Bar = 50 μm.