Figure 5. Schematic presentation of the two B. cenocepacia H111 QS circuitries.
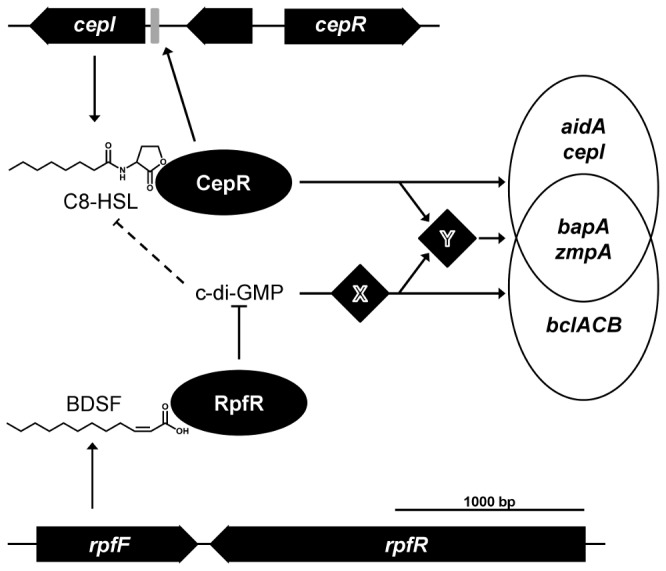
The CepI/CepR system consists of the AHL synthase CepI directing the synthesis of C8-HSL, and of the transcriptional regulator CepR. The RpfF/RpfR system consists of RpfF which directs the synthesis of BDSF, and of its cognate receptor RpfR. Upon binding of BDSF to RpfR the c-di-GMP phosphodiesterase activity of the protein is stimulated and as a consequence the intracellular c-di-GMP level is lowered. The two QS systems operate in parallel to control specific as well as overlapping sets of genes. Our working model assumes an unknown c-di-GMP receptor protein × that stimulates transcription of target genes. Alternatively, the two QS cascades converge and control the expression or the activity status of an unknown common regulator Y, which in turn regulates expression of target genes. C-di-GMP has a negative regulatory effect on AHL levels via an unknown mechanism (depicted by the dashed line).
