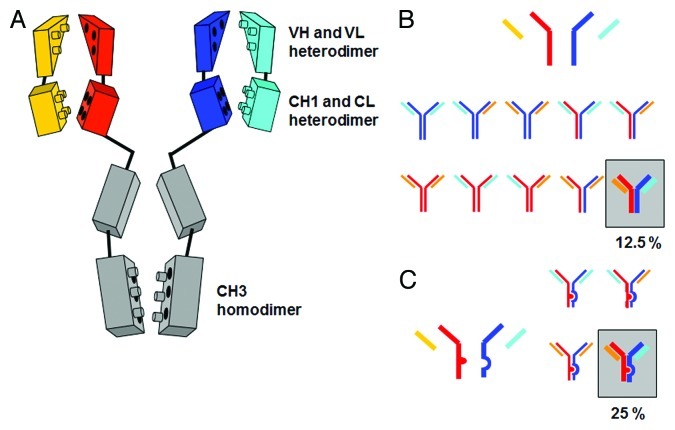
Figure 1. (A) Schematic depiction of the homo- and heterodimerization interfaces between light- and heavy-chain domains leading to mixtures when expressed simultaneously. (B) Chain association issue when co-expressing two different antibody heavy and light chains in one cell line, assuming random chain association (Quadroma). In total, 24 = 16 combinations are possible. Of those, 6 are identical; thus, a purely statistical association leads to 6 tetramers that occur twice (each 12.5% yield) and 4 tetramers that occur once (each 6.25%). The desired bispecific antibody makes up statistically 12.5% of the total yield. (C) Light chain association issue when co-expressing two different antibody light chains in one cell line, assuming random chain association. Heavy chain heterodimerization is enforced using KiH technology. The desired bispecific antibody makes up statistically 25% of the total yield.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.