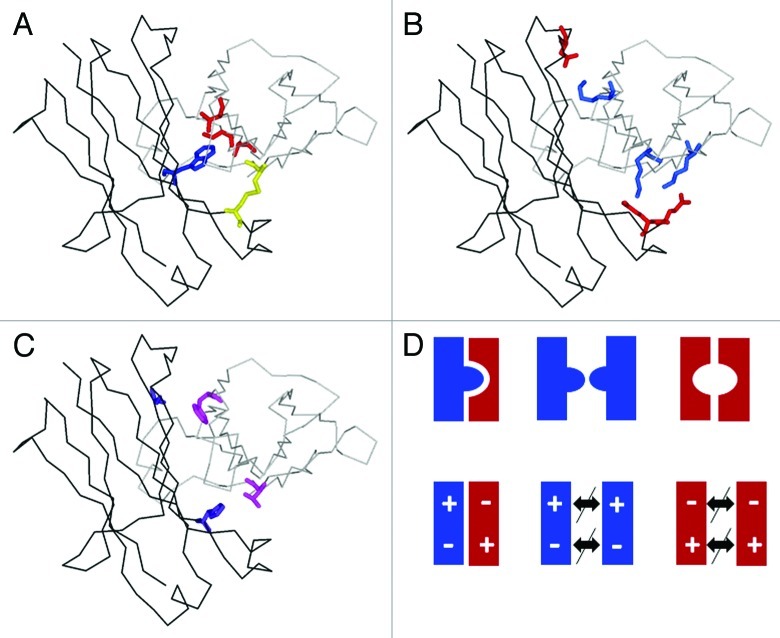
Figure 3. Enforcing correct heavy chain association by CH3-CH3 interface modification. Structural model of heterodimeric Fc (one CH3 domain as black line, the other as gray line) with (A) KiH mutations and S-S stabilization (1 knob mutation, blue; 3 hole mutations, red; one disulfide bridge, yellow).25 (B) charged residues located at the CH3-CH3 interface (Glu, Asp, red; Lys blue) that can typically be used to enforce heterodimerization by appropriate exchange as shown by Amgen and Chugai. (C) optimal variant (4 mutations, purple and magenta) obtained by Xencor. (D) schematic representation of (from left) the desired heterodimer and the two unwanted homodimers obtained by the KiH method (top) or use of electrostatic steering (bottom).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.