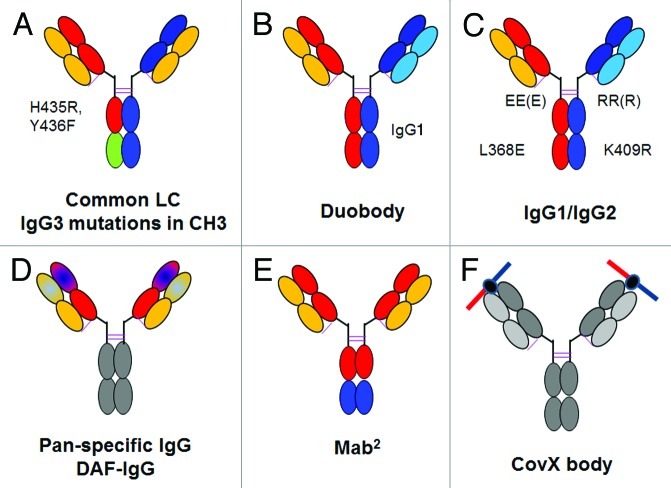
Figure 5. Overview of bispecific heterodimeric IgG antibodies. (A) Common light chain bispecific antibody with H435R Y436F mutation to allow depletion of hole-hole antibodies. (B) Duobody approach based on IgG4 Fab arm exchange with in vitro assembly. (C) Bispecific heterodimeric IgG1/IgG2 with EEE/RRR mutations with in vitro assembly. (D) Dual-acting Fab (DAF) IgG or pan-specific monoclonal antibodies. (E) Mab2 approach with introduction of additional binding sites in the Fc region of an IgG antibody. (F) CovX body approach with fusion of a bispecific binding peptide into the active center of a catalytically active IgG antibody. The bispecific binding peptide is indicated on the top. For a more detailed description, refer to the text.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.