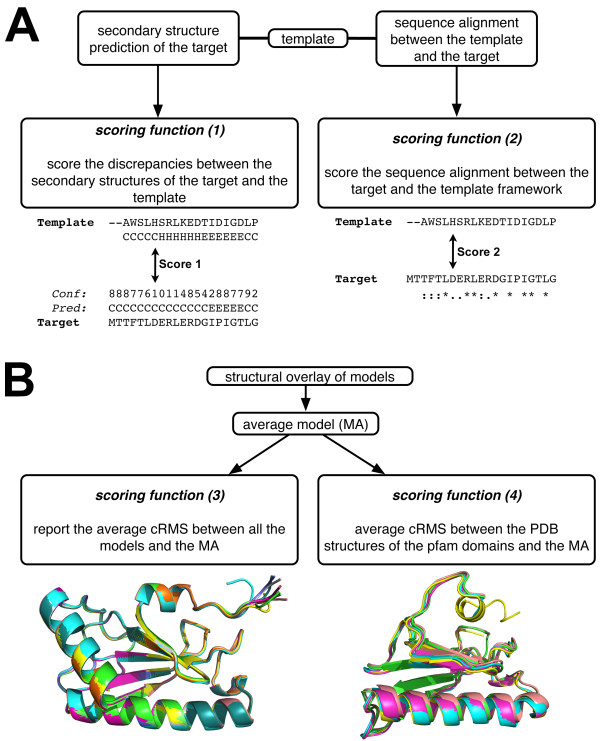
Figure 1.
Flowchart for computing the H-factor. A. The scoring functions (1) and (2) are sequence-based. The score (1) compares the secondary structure prediction for the target sequence with the actual secondary structure assignment of the template protein. As an example, an extract of a sequence alignment between a template and a target is represented. The secondary structures of the template are indicated underneath the sequence of the template (C: coil, H: helix). Above the sequence of the target is indicated the secondary structure prediction for the target along with its confidence factor returned by PSIPRED. Score (2) evaluates the sequence similarity between the target and template sequence. B. The scoring functions (3) and (4) evaluate the structural models: score (3) quantifies the structural diversity among the models, while score (4) identifies the pfam domains in the target protein, collects the structures of these domains from the models to be tested, and compares these structures with those observed for the same domains in the PDB.