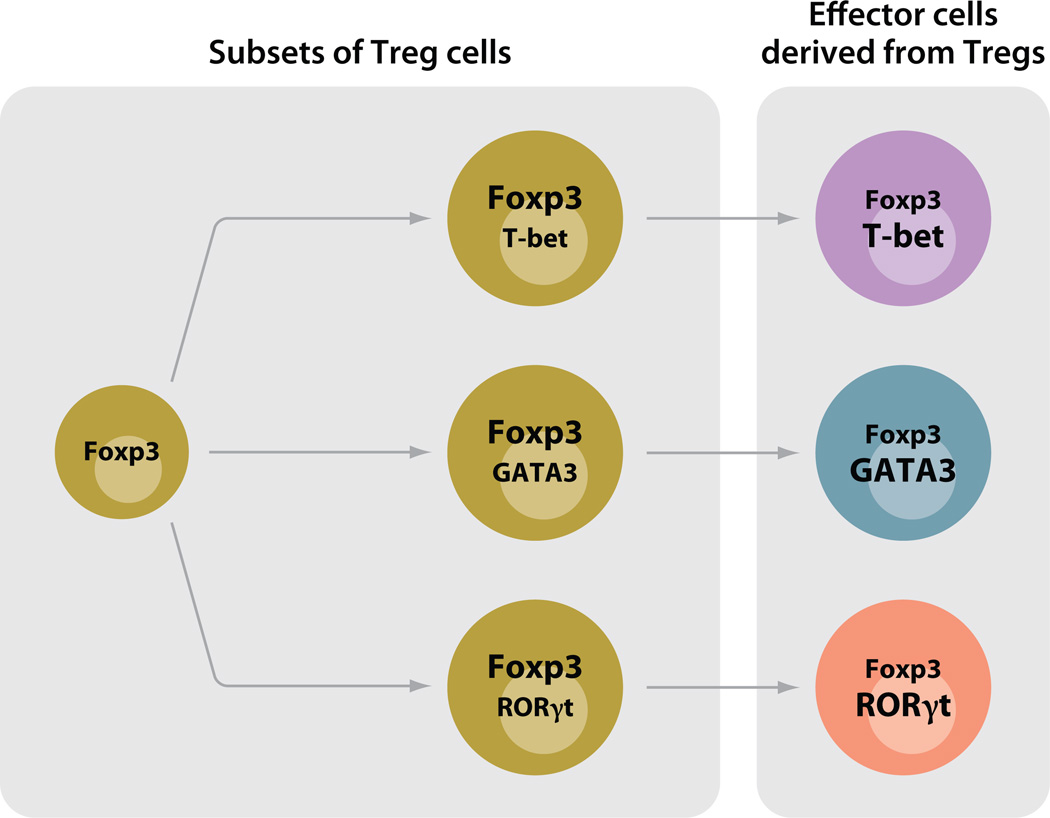
Figure 6.
Complexity of Tregs. Foxp3 is the master regulator for Tregs. Recent reports and our unpublished data show that the transcription factors for Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells, T-bet, GATA3, and RORγt, respectively, can also be coexpressed in some Tregs (36, 113, 182). A relatively high expression ratio of Foxp3 over another master transcription factor prevents the induction of effector cytokines. Different combinations of transcription factors subdivide the Tregs with possible distinct regulatory functions. In some cases, the level of Foxp3 expression may fall, leading to expression of effector cytokines controlled by the other master regulator expressed by the cell. Effector cells derived from Tregs, because of their unique antigen specificity, may participate in normal immune responses to infections or contribute to autoimmune diseases (287).