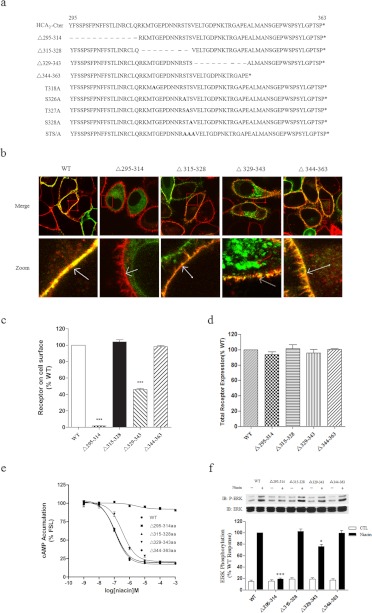
Fig. 1.
Expression and functional characterization of C-terminal deletion mutants of human HCA2. a, sequence comparison of the COOH domains of the wild-type and mutant HCA2 constructs. A series of mutants were made in the carboxyl terminus of HCA2 using overlap polymerase chain reaction as described under Materials and Methods. The deleted amino acids are indicated with a dash (–). b, HEK-293 cells stably expressing WT or mutant HCA2-EGFP (green) were stained with DiI (5 μM, red), fixed, and examined by confocal microscopy. c and d, HEK-293 cells transiently transfected with WT or mutant FLAG-HCA2 were used to assess cell surface receptor levels and total cell receptor levels by ELISA (see Materials and Methods). e, cAMP accumulation in HEK-293 cells transiently cotransfected with HCA2 or HCA2 mutants and pCRE-Luc was determined in response to treatment with forskolin and niacin. f, activation of ERK1/2 in HEK-293 cells stably expressing HCA2 or HCA2 mutants by a challenge with 200 μM niacin for 5 min. Error bars represent the S.E.M. for four replicates. Data were analyzed using Student's t test (*, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001). All data shown are representative of at least three independent experiments. IB, immunoblot; CTL, control.