Figure 1. PARP-14 and its activity are required for optimal Th2 differentiation.
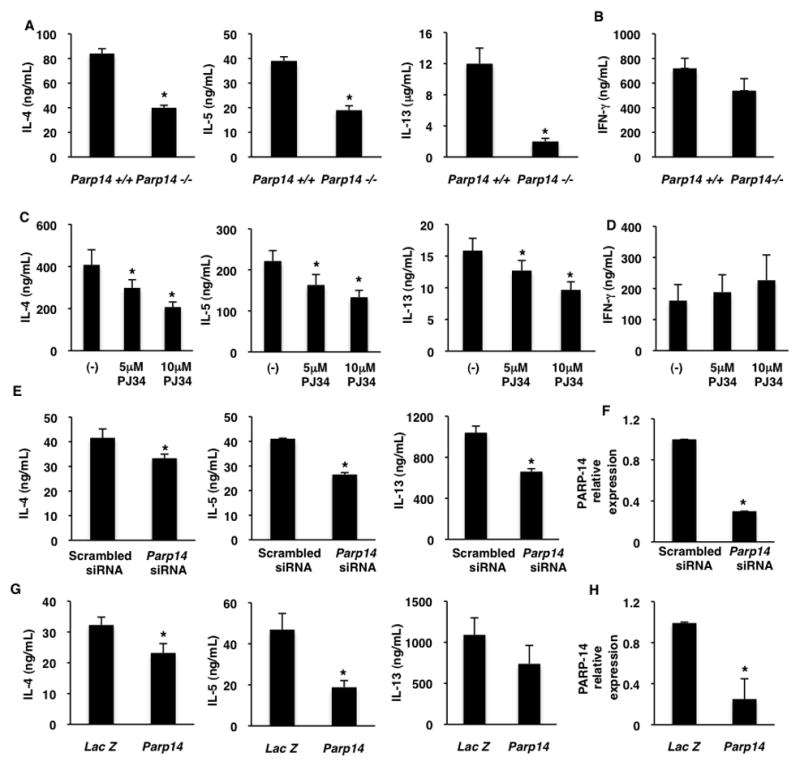
(A–B) Naïve T cell from Parp14−/− and WT mice were cultured under Th2 (A) and Th1 (B) conditions. differentiated cells were re-stimulated and the indicated cytokines were measured by ELISA. (C–D) CD4+CD62Lhigh T cells were cultured under Th2 (C) and Th1 (D) skewing conditions in the presence or absence of PJ34 for 7 days. The indicated cytokines were measured. (E–F) Naïve T cells were nucleofected with the indicated siRNA and then cultured under Th2 conditions for 5 days. Cytokines and PARP-14 expression were measured as indicated. (G–H) Short Hairpins specific for PARP-14 or LacZ were retrovirally transduced into activated T cells and cultured under Th2 conditions. Cytokines and PARP-14 expression were measured as indicated. The results are mean (± SEM) of three different experiments. An asterisk on the graphs indicates a p value of ≤ 0.05 when compared to controls.
