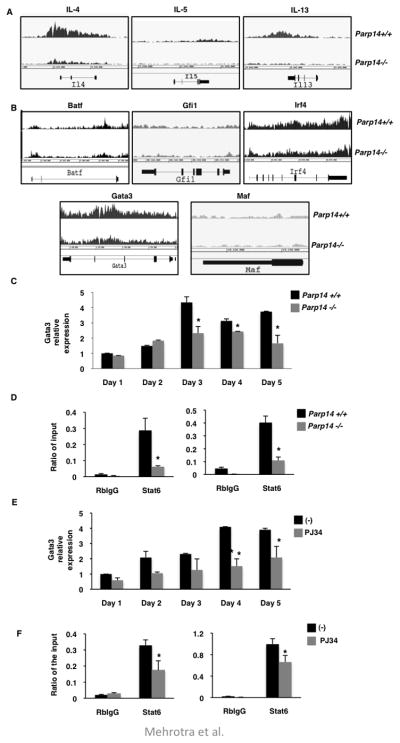
Figure 5. PARP-14 and activity associated with it is required for ambient GATA-3 expression.
Naïve CD4+ T cells from Parp14+/+ and Parp14−/− mice were differentiated under Th2 conditions and then re-stimulated in the presence of IL-4. ChIP-Seq was performed on these cells using an antibody directed towards the active form of RNA Polymerase II antibody. Screen capture views of ChIP-seq signal profile maps for the indicated cytokines (A) and transcriptional factors (B) from the genome browser are shown. (C) CD4+ cells isolated from Parp14+/+ and Parp14−/− mice were cultured for 5 days under Th2 conditions and Gata3 mRNA levels was measured on each day. (D) CD4+ cells were activated in the presence of IL-4 for 1 hr. ChIP was performed using indicated antibodies. The immunoprecipitated DNA was evaluated for Gata3 promoter fragments, S4 (left graph) and S7 (right graph). (E) CD4+ cells were cultured under Th2 conditions with or without 10μM PJ34. Transcripts of Gata3 were quantified using qPCR. (F) CD4+ T cells isolated from WT mice were stimulated with IL-4 in the presence or absence of 10μM PJ34 for 1 hr. ChIP experiments were performed as in (D). The results are mean (± SEM) of three independent experiments. The asterisk indicates a p value of ≤ 0.05 when compared to controls.