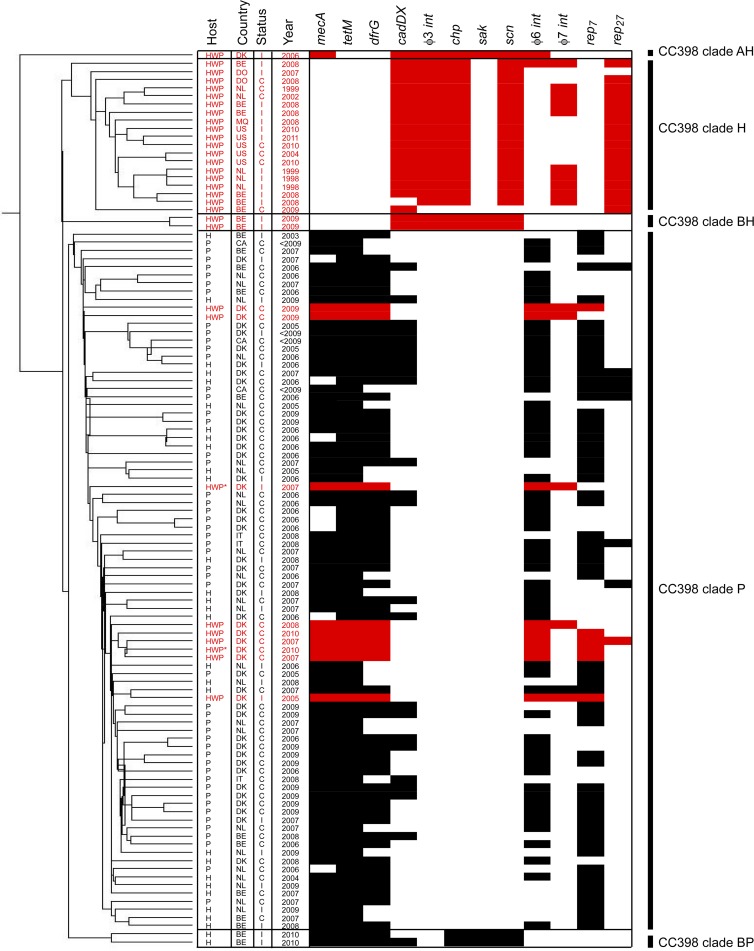
Fig 1.
Microarray clustering analysis of CC398 isolates based on 11,715 60-mer oligonucleotides representing MGE genes. The clustering on the left shows the evolutionary relatedness of the isolates. For each isolate, the host origin (human with pig contact = H, pig = P, and human without pig contact = HWP), country origin (Belgium = BE, Canada = CA, Denmark = DK, Dominican Republic = DO, Italy = IT, Martinique = MQ, The Netherlands = NL, and United States = US), status (colonization = C and infection = I), and year of isolation is shown. Isolates from humans without pig contact are highlighted in red, while isolates from pigs and humans with pig contact are shown in black. Multiple MGEs varied between isolates, and representative genes of those MGEs with the strongest association with a clade are shown as present (black/red boxes) or absent (white boxes) Each MGE gene was significantly associated (P < 0.05, χ2 test) with either the major pig-associated CC398 clade (clade P) or the major human-specific CC398 clade (clade H). Two humans without pig contact may have had previous exposure to reservoirs of pig bacteria; they are denoted with an asterisk (HWP*).