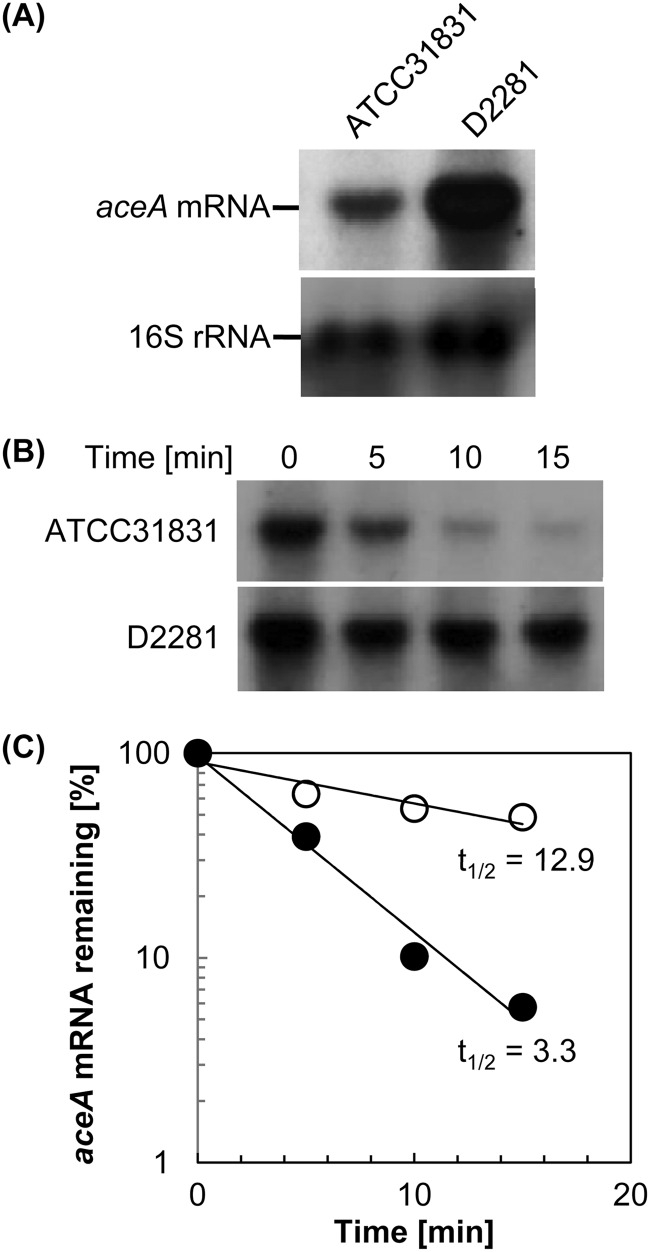
Fig 2.
Increased stability of aceA mRNA in the ΔrneG mutant. (A) Intracellular levels of aceA mRNA and 16S rRNA in ATCC 31831 (wild type) and D2281 (ΔrneG) strains. Total RNAs from ATCC 31831 and D2281 were analyzed by Northern hybridization, as described in Materials and Methods, using specific probes for aceA mRNA and 16S rRNA. (B) Measurement of the half-lives of aceA mRNA in the ATCC 31831 and D2281 strains. Rifampin was added to exponentially growing cultures of ATCC 31831 and D2281 at time zero, and at the indicated times, total RNAs were isolated and analyzed by Northern hybridization using a specific probe for aceA mRNA. (C) The intensities of the hybridized bands in Fig. 2B were quantified with Just TLC software and the half-life (t1/2) (min) of aceA mRNA was calculated. Filled circles, ATCC 31831; open circles, D2281. The half-lives shown are representative of those from three independent rifampin chase experiments with comparable results.