Abstract
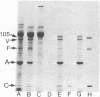
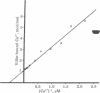
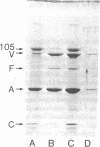
The microvillus core-filament bundle from intestinal epithelial cells is a highly ordered structure containing actin and four major associated proteins. Two of these, villin and calmodulin, bind calcium ions (Kd approximately 10(-6) M) in the physiologically important range. Because ethylene glycol bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid is present throughout the purification and the isolated cores contain levels of calcium substoichiometric to calmodulin, the protein is bound in the structure without calcium saturation. 10-[3-(4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl]-2-trifluoromethylphenothiazine, a calmodulin-specific drug, removes the protein from the cores without visibly affecting their ultrastructure. Calmodulin-depleted cores rebind exogenously supplied brain calmodulin. Although the core filaments are stable when the calcium level is less than 10(-7) M, they dissassemble when it is greater than 10(-6) M. This appears to be due to the calcium-sensitive allosteric transition of villin from an F-actin bundling protein to an F-actin severing protein. The actions of the two calcium-binding proteins, villin and calmodulin, are discussed in terms of the calcium sensitivity of the filament bundle. We suggest that villin may act as a calcium-sensitive factor regulating microfilament assembly and disassembly and that calmodulin serves as a buffer modulating the free calcium concentration. This hypothesis may explain some aspects of the physiological process of calcium uptake in the intestine and of the effects of calcium fluxes on the submembranous organization of microfilaments in other cells and tissues.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen B., Osborn M., Weber K. Specific visualization of the distribution of the calcium dependent regulatory protein of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (modulator protein) in tissue culture cells by immunofluorescence microscopy: mitosis and intercellular bridge. Cytobiologie. 1978 Aug;17(2):354–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Fimbrin, a new microfilament-associated protein present in microvilli and other cell surface structures. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):335–340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Localization of actin and microfilament-associated proteins in the microvilli and terminal web of the intestinal brush border by immunofluorescence microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):839–845. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Purification of microvilli and an analysis of the protein components of the microfilament core bundle. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Oct 15;116(2):397–407. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90463-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Villin is a major protein of the microvillus cytoskeleton which binds both G and F actin in a calcium-dependent manner. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Villin: the major microfilament-associated protein of the intestinal microvillus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2321–2325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Burchell A., Foulkes J. G., Cohen P. T., Vanaman T. C., Nairn C. Identification of the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein as the fourth subunit of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80772-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca H. F. Vitamin D and calcium transport. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:356–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipolo R., Requena J., Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J., Scarpa A., Tiffert T. Ionized calcium concentrations in squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Apr;67(4):433–467. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellewell S. B., Taylor D. L. The contractile basis of ameboid movement. VI. The solation-contraction coupling hypothesis. J Cell Biol. 1979 Dec;83(3):633–648. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C. L., Mooseker M. S., Graves T. A. Brush-border calmodulin. A major component of the isolated microvillus core. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):916–923. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilundain A., Naftalin R. J. Role of Ca(2+)-dependent regulator protein in intestinal secretion. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):446–448. doi: 10.1038/279446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson G. A., Jr, Vanaman T. C. Calcium-dependent affinity chromatography of calmodulin on an immobilized phenothiazine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):1048–1056. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91932-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Lindberg U. Actin is the naturally occurring inhibitor of deoxyribonuclease I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4742–4746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin R. M., Weiss B. Binding of trifluoperazine to the calcium-dependent activator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Jul;13(4):690–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannherz H. G., Goody R. S. Proteins of contractile systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:427–465. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. T., Burgess D. R. Identification and organization of the components in the isolated microvillus cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1979 Dec;83(3):667–673. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.3.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimura N., Asano A. Ca2+-sensitive gelation of actin filaments by a new protein factor. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):44–48. doi: 10.1038/282044a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S. Brush border motility. Microvillar contraction in triton-treated brush borders isolated from intestinal epithelium. J Cell Biol. 1976 Nov;71(2):417–433. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S., Pollard T. D., Fujiwara K. Characterization and localization of myosin in the brush border of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):444–453. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S., Tilney L. G. Organization of an actin filament-membrane complex. Filament polarity and membrane attachment in the microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):725–743. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piascik M. T., Wisler P. L., Johnson C. L., Potter J. D. Ca2+-dependent regulation of guinea pig brain adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4176–4181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. Contractile proteins in cell structure and function. Annu Rev Med. 1978;29:427–457. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.29.020178.002235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Dedman J. R., Brinkley B. R., Means A. R. Calcium-dependent regulator protein: localization in mitotic apparatus of eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1867–1871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff D. J., Poirier P. G., Brostrom C. O., Brostrom M. A. Divalent cation binding properties of bovine brain Ca2+-dependent regulator protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4108–4117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yerna M. J., Dabrowska R., Hartshorne D. J., Goldman R. D. Calcium-sensitive regulation of actin-myosin interactions in baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):184–188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Stossel T. P. Control of cytoplasmic actin gel-sol transformation by gelsolin, a calcium-dependent regulatory protein. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):583–586. doi: 10.1038/281583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]