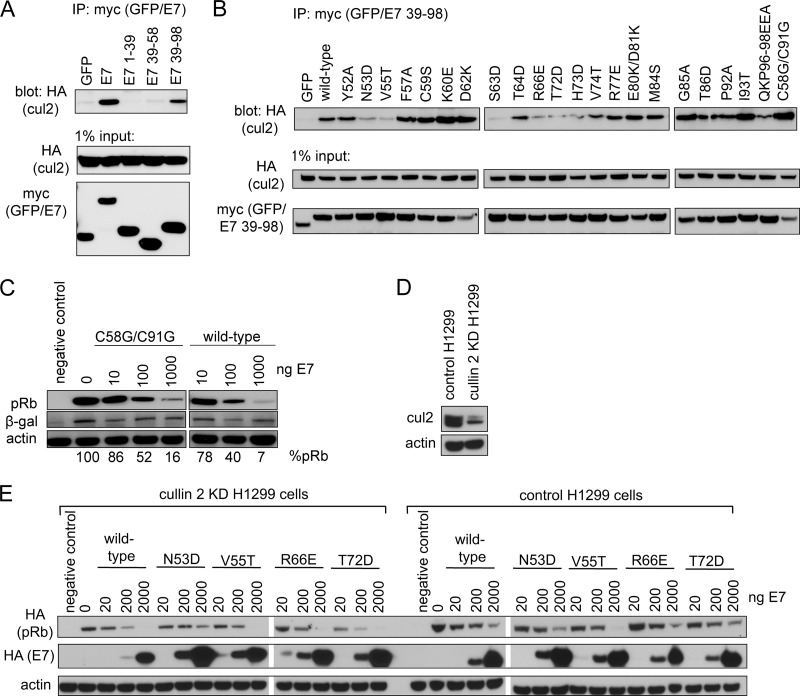
Fig 3.
Contribution of cullin 2 complex to E7-induced pRb degradation. (A) CR3 of E7 is necessary and sufficient to bind cullin 2. HT1080 cells were transfected with an equal ratio of hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged cullin 2 expression plasmid to either myc-GFP or myc-GFP-fused E7 fragment (as indicated). Twenty-four h posttransfection, cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-myc antibody, followed by Western blotting for cullin 2 with anti-HA antibody. (B) Cullin 2 binding capacity of CR3 mutants. HT1080 cells were cotransfected with HA-tagged cullin 2 and either myc-GFP or myc-GFP-fused E7 39-98 (wild type or indicated mutant). Coimmunoprecipitation was carried out as described above. (C) The C58G/C91G mutant retains the ability to degrade pRb. Saos2 cells were transfected with 1 μg pRb, 0.1 μg β-galactosidase, and the indicated amounts of full-length wild-type or C58G/C91G mutant E7. Samples were collected 48 h posttransfection, and the steady-state levels of pRb were analyzed by Western blotting. %pRb indicates the relative amount of remaining pRb in each lane. (D) Cullin 2 levels in H1299 control and H1299 cullin 2 knockdown (KD) cells. The levels of endogenous cullin 2 present in H1299 control and H1299 cullin 2 KD cells were analyzed using anti-cul2 antibody. (B) Dependence of E7 on cullin 2 for pRb degradation. pRb degradation assays were conducted in cullin 2 KD and control cells for indicated E7 mutants, as described in Materials and Methods.