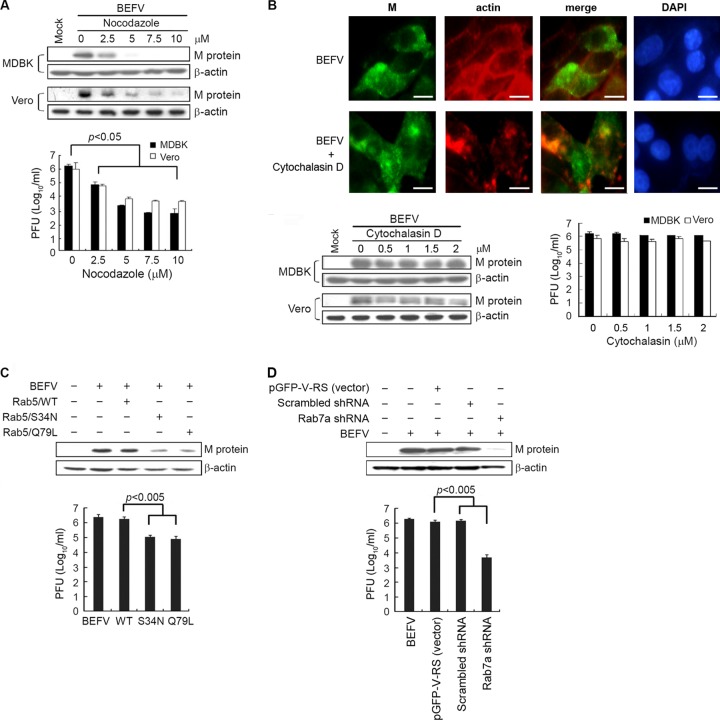
Fig 4.
Effect of inhibition of BEFV infection by the disrupted microtubule assemble and functional repression of Rab5 or Rab7a. (A and B) MDBK and Vero cells were pretreated with different concentrations of nocodazole (A) or cytochalasin D (B) or with DMSO as a mock control for 1 h and then infected with BEFV at an MOI of 2 for 24 h. The cells were harvested at 24 hpi. The level of M protein of BEFV and β-actin was examined by Western blotting. The progeny virus titer of BEFV was examined by plaque formation assay. To demonstrate that cytochalasin D was active at the concentration used, rhodamine phalloidin was used to stain cytochalasin D-treated cells or BEFV-infected and cytochalasin D-treated cells (B, upper panel). MDBK cells were pretreated with cytochalasin D (1 μM) for 1 h before infection with BEFV at an MOI of 2. (C and D) MDBK cells transfected with Rab5 DN mutants (C) or Rab7a shRNAs (D) for 24 h were infected with BEFV at an MOI of 2 for 24 h. The level of BEFV M protein and supernatants of BEFV-infected cells were analyzed by Western blotting and viral titration, respectively. The results are from triplicate experiments; error bars indicate the means ± standard deviations.