Figure 10.
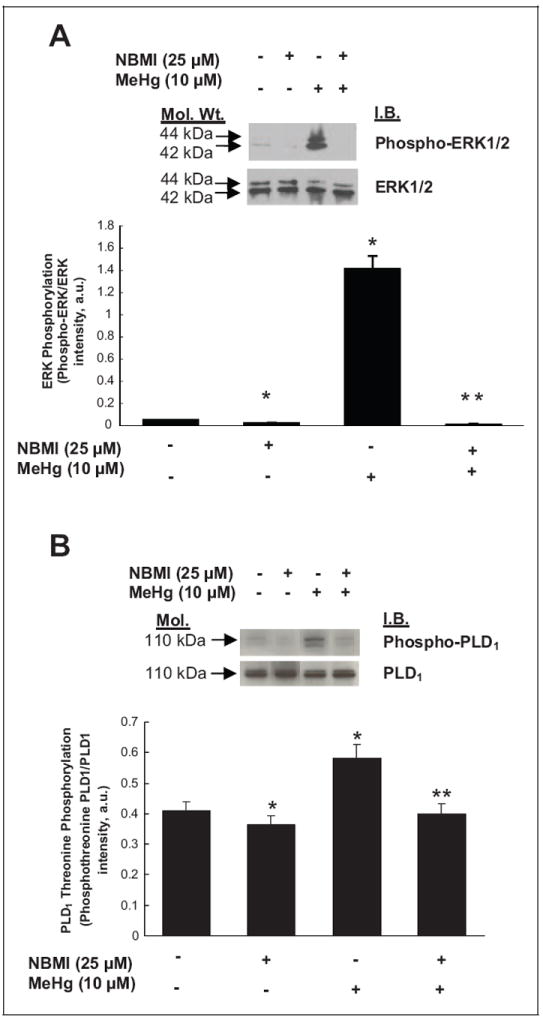
N,N′-bis(2-Mercaptoethyl)isopthalamide (NBMI) attenuates the mercury-induced phosphorylation of extracellular-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and phospholipase D1 (PLD1) in mouse aortic endothelialcells (MAECs). The MAECs (5 × 105 cells/35 mm dish) pretreated with minimal essential medium (MEM) alone or MEM containing NBMI (25 μmol/L) for 1 hour were treated with MEM alone or MEM containing methylmercury (10 μmol/L) for 1 hour. Following treatment, proteins in cell lysates were subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Western blotting with (A) phospho-ERK1/2-specific, ERK1/2-specific, (B) phosphotheonine-PLD1-specific and PLD1-specific monoclonal antibodies. The intensity of the protein bands were digitally determined as described in Materials and Methods section. Data represent mean ± standard deviation (SD) calculated from 3 independent experiments. *Significantly different at P < .05 as compared to cells treated with MEM alone. **Significantly different at P < .05 as compared to cells treated with MEM containing mercury alone.
